Imagine a sharp, shooting pain that erupts in your lower back, radiating down your leg. It’s so intense you can barely move. You might be experiencing the debilitating effects of a left subarticular disc protrusion. This condition affects the intervertebral discs, those cushions that act as shock absorbers between your vertebrae. When one of these discs protrudes, it can put pressure on the surrounding nerves, causing pain, numbness, and weakness.

Image: captionsbeautifulus.blogspot.com
This article delves into the world of left subarticular disc protrusions, providing a comprehensive explanation of this condition and exploring the various treatment options available. Whether you’re grappling with the pain yourself or seeking more information for a loved one, this guide will equip you with knowledge to understand your options and navigate this challenging experience.
Understanding the Anatomy of a Problem: The Intervertebral Disc
To grasp the nature of a left subarticular disc protrusion, we need to understand the anatomy of the intervertebral discs. Picture these discs as small, jelly-filled donuts, each sandwiched between two vertebrae. They consist of two parts:
- Annulus fibrosus: This tough, outer ring acts like the tire of a donut, providing structural support and stability to the disc.
- Nucleus pulposus: The “jelly” inside the donut, this soft, gel-like center is responsible for absorbing shocks and allowing the spine to move freely.
When the annulus fibrosus weakens or tears, the nucleus pulposus can bulge or even protrude outward, pushing against the surrounding nerves. When this occurs on the left side of the spine, specifically in the area adjacent to the articulation of two vertebrae, it’s referred to as a left subarticular disc protrusion.
The Roots of the Problem: What Leads to Disc Protrusion?
While the exact cause of a left subarticular disc protrusion isn’t always clear, several factors can contribute to its development:
- Age: As we age, the discs lose water content, becoming less resilient and more prone to degeneration.
- Genetics: Some individuals possess a genetic predisposition for disc degeneration, making them more susceptible to these conditions.
- Repetitive Strain: Jobs requiring frequent lifting, twisting, or bending can place undue stress on the spine, increasing the risk of disc protrusions.
- Injury: A sudden injury, such as a fall or car accident, can strain or rupture the disc.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts additional stress on the spine, making disc degeneration more likely.
- Poor Posture: Chronic poor posture can put strain on the discs, leading to degeneration.
Living with the Pain: Symptoms of a Left Subarticular Disc Protrusion
The pain associated with a left subarticular disc protrusion can be a significant source of distress. The location and severity of the pain can vary, but common symptoms include:
- Lower back pain: Often intense, sharp, or shooting pain that may worsen with movement.
- Sciatica: Pain that radiates down the leg, usually affecting the same side as the disc protrusion. This pain can follow the sciatic nerve, running down the back of the leg and into the foot.
- Numbness and tingling: A feeling of pins and needles or numbness in the leg, foot, or toes.
- Weakness: Muscle weakness in the leg or foot.
- Limited range of motion: Difficulty bending, straightening, or twisting your back.
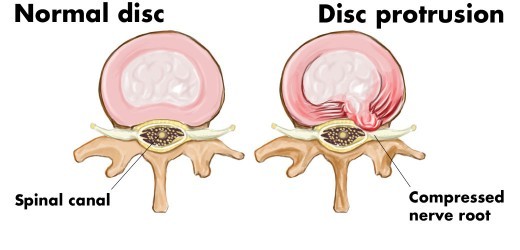
Image: dumbbellsanddiapers.com
Diagnosing the Source of the Discomfort: Testing for a Left Subarticular Disc Protrusion
If you’re experiencing symptoms consistent with a left subarticular disc protrusion, it’s essential to seek medical attention. Your healthcare provider will conduct a comprehensive physical exam, asking about your symptoms, medical history, and lifestyle.
Imaging tests are often used to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of the disc protrusion:
- X-rays: X-rays can reveal changes in the alignment of your spine and help rule out other conditions. However, X-rays alone may not show a disc protrusion.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): This advanced imaging test provides detailed images of soft tissues, including the spinal discs, nerves, and surrounding structures. It’s the most accurate tool for diagnosing disc protrusions and determining the extent of compression on the nerve roots.
Choosing the Right Path to Recovery: Treatment Options for Disc Protrusion
Once a left subarticular disc protrusion is diagnosed, your healthcare provider will recommend a treatment plan tailored to your specific needs and symptoms. The goal of treatment is to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and restore function to the affected area.
The treatment approach can vary depending on the severity of the protrusion and your individual circumstances.
Conservative Approaches: Starting with the Basics
Conservative treatment options aim to manage pain and inflammation without surgery. These approaches may include:
- Rest: Restricting activities that aggravate your pain. This may involve limiting bending, twisting, and lifting.
- Pain medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or naproxen, or prescription pain medications for more severe pain.
- Physical therapy: A physical therapist can teach you stretches, exercises, and posture correction techniques to strengthen your muscles, improve flexibility, and relieve pain.
- Heat/Cold therapy: Applying heat or cold packs to the affected area can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Injections: In some cases, your healthcare provider may recommend steroid injections to reduce inflammation and swelling around the nerve roots.
When Conservative Approaches Aren’t Enough: Surgical Intervention
Surgery for a left subarticular disc protrusion is generally considered an option when conservative treatment methods are ineffective or the symptoms are severe.
- Discectomy: Surgical removal of the protruded disc material to relieve pressure on the nerve.
- Fusion: Surgical procedure that involves permanently joining two vertebrae, often performed for spinal instability.
It’s important to note that surgery carries its own risks and complications. Discuss your options and potential risks thoroughly with your healthcare provider before making a decision.
Expert Insights: Advice from the Professionals
- Dr. Emily Anderson, Neurosurgeon: “Many left subarticular disc protrusions improve with conservative treatment. The majority of patients can achieve significant pain relief and restored functionality through physical therapy, pain medication, and lifestyle adjustments.”
- Dr. Michael Brown, Physical Therapist: “It’s crucial to engage in regular low-impact exercises like swimming or walking to strengthen your back and core muscles. This helps stabilize the spine and reduce strain on the discs.”
- Dr. Sarah Davis, Chiropractor: “Proper posture and ergonomic practices can play a vital role in preventing future disc problems. Ensuring you have good posture while sitting and lifting objects can significantly reduce stress on your spine.”
Left Subarticular Disc Protrusion
https://youtube.com/watch?v=JvlqtX-183U
Moving Forward: Taking Charge of Your Back Health
A left subarticular disc protrusion can significantly impact your quality of life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available, you can be an active participant in your recovery journey.
Seek medical attention if you suspect a disc protrusion, follow your doctor’s recommendations, and actively engage in physical therapy and lifestyle modifications. With the right approach, you can work towards pain relief, functional improvement, and a healthier back. Remember, you are not alone in this journey.






