Have you ever looked at the electrical wiring in your home and wondered about the mysterious numbers and markings? You might have noticed a common labeling – 14/2 wire. This seemingly simple marking holds the key to understanding a crucial part of your home’s electrical system. But before we dive into the intricacies of 14/2 wire, let’s address the question that might be buzzing in your mind: Why should you care about this seemingly small detail? The answer is simple: knowing about 14/2 wire can ensure the safety and efficiency of your home’s electrical system. It can even help you make informed decisions when tackling DIY projects or working with an electrician.

Image: homejustright.com
This article will serve as your comprehensive guide to 14/2 wire. We’ll explore its construction, applications, and what makes it such a fundamental element in residential wiring. By the end, you’ll understand the importance of 14/2 wire and its role in securing the electrical foundation of your home.
Deconstructing the Code: What Does 14/2 Wire Mean?
The term “14/2 wire” is actually a shorthand for describing a specific type of electrical cable. This seemingly simple code packs a lot of information. Let’s break it down:
-
14: This number refers to the American Wire Gauge (AWG) of the wire’s conductor. The lower the AWG number, the thicker the wire. In this case, 14 AWG signifies a relatively thin wire commonly used for low-voltage circuits in residential settings.
-
2: This number indicates the number of conductors within the cable. So, 14/2 wire has two insulated wires running together.
14/2 wire is often referred to as ” Romex”, a brand name that has become synonymous with this type of cable. However, it’s important to note that ” Romex” is a trademark, and other manufacturers produce similar cables.
The Anatomy of 14/2 Wire: Unraveling the Components
Let’s take a closer look at what makes up 14/2 wire:
-
Conductor: The heart of the wire is the copper conductor, which carries the electrical current. In 14/2 wire, this conductor is typically made of bare, solid copper wire, though stranded copper is also available.
-
Insulation: The copper conductor is wrapped in an insulating layer, usually made of PVC (polyvinyl chloride). The insulation prevents the live wires from touching each other and providing a path for electricity to flow where it shouldn’t. The color of the insulation is crucial: the white wire typically carries the neutral current, the black wire carries the hot current, and the bare copper wire is the ground wire.
-
Sheath: The final layer is a protective outer sheath that holds the insulated wires together. This outer layer is often made of PVC and is typically white or gray, though other colors may be available.
Where Does 14/2 Wire Shine? Common Applications in Residential Wiring
14/2 wire is a versatile electrical workhorse, finding its way into countless residential applications. Here are some common scenarios where you’ll encounter 14/2 wire:
-
Lighting Circuits: Whether you’re illuminating your kitchen countertops or adding ambiance to your living room, 14/2 wire is the go-to choice for most standard lighting circuits. Its capacity to handle the typical low-voltage requirements of light fixtures makes it a reliable option for these installations.
-
Receptacle Circuits: From plugging in your phone charger to powering appliances like a coffee maker, 14/2 wire is frequently used to create electrical outlets in your home. These circuits typically require a relatively low current, making 14/2 wire a suitable and cost-effective choice.
-
Ceiling Fans: 14/2 wire is often the go-to option for wiring ceiling fans. Its ability to handle the specific power requirements of ceiling fans makes it a convenient and reliable solution.
-
Small Appliances: 14/2 wire is used to power a variety of small appliances like microwave ovens, refrigerators, and dishwashers. As long as the appliance’s power draw aligns with the wire’s capacity, 14/2 wire is a practical choice.
-
Basement or Attic Wiring: Adding extra electrical outlets in your basement or attic? 14/2 wire is often the preferred choice for these projects, due to its versatility and ability to suit most typical wiring requirements.
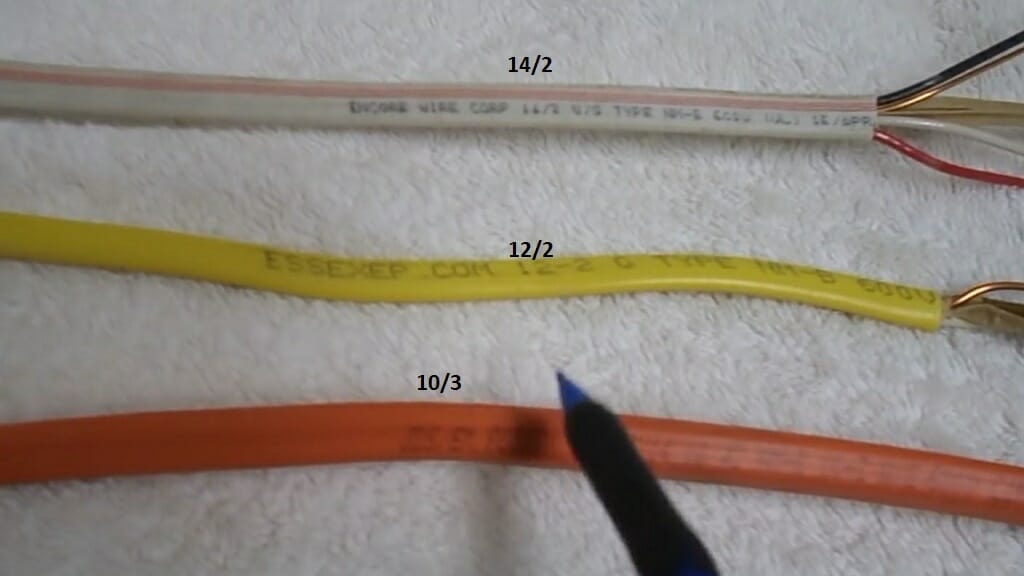
Image: toolsweek.com
Choosing the Right Wire for the Job: When to Consider Alternatives
While 14/2 wire is a versatile and reliable option, it’s not always the ideal choice for every application. Here are some situations where other wires might be better suited:
-
High-Voltage Circuits: For applications that require higher electrical loads, such as running an electric stove or a hot tub, 14/2 wire might not be sufficient. Larger gauge wires with greater current carrying capacity, like 12/2 or 10/2 wire, might be required for these circuits.
-
Specialty Circuits: Certain applications, such as wiring electric baseboard heaters, might require a specific type of wire, such as TW (thermo-plastic insulated wire) or UF (underground feeder) wire.
-
Outdoor Applications: While 14/2 wire can be used in some outdoor applications, it’s crucial to choose a cable specifically designed for outdoor use. Outdoor-rated wiring is designed to withstand weather elements and prevent damage.
Safety First: Understanding the Importance of Grounding
One of the most critical aspects of electrical wiring is grounding. The ground wire in 14/2 wire (the bare copper wire) plays a vital role in ensuring electrical safety. Here’s why:
-
Protection Against Electrical Shocks: If a live wire comes into contact with a metal surface, such as a faulty appliance housing, the ground wire offers a safe path for the electricity to flow to the earth. This prevents the metal surface from becoming energized and potentially causing an electrical shock.
-
Protecting Your Devices: In the event of a short circuit or ground fault, the ground wire provides a path for excessive current to flow to the ground, minimizing damage to electrical devices and potentially preventing a fire.
Finding the Right Electrician: Seeking Professional Expertise
While tackling some small DIY electrical projects might seem tempting, working with electrical systems can be dangerous. It’s essential to rely on qualified and licensed electricians for any major wiring projects or if you’re unsure about a particular aspect of electrical work.
Here are some tips for finding a reputable electrician:
-
Check Licensing and Certifications: Ensure the electrician is licensed and certified in your area.
-
Read Testimonials and Reviews: Look at customer reviews and testimonials to gauge the electrician’s expertise and professionalism.
-
Get Multiple Quotes: Get quotes from several electricians to compare pricing and ensure you’re getting a fair deal.
What Is 14/2 Wire Used For
Conclusion: Empowering You with Knowledge about 14/2 Wire
Understanding the role of 14/2 wire in your home’s electrical system can empower you to make informed decisions about your electrical needs. Whether you’re tackling a DIY project or working with a professional electrician, knowing about this versatile and ubiquitous wire will help you ensure the safety and efficiency of your home’s electrical infrastructure.
Remember that safety should always be your top priority when working with electricity. If you’re unsure about any aspect of electrical work, consult a qualified electrician to avoid potential dangers.
Now that you’ve equipped yourself with this knowledge about 14/2 wire, we encourage you to share your experiences or ask any remaining questions in the comments section below. Let’s create a community of informed homeowners who understand the essential elements of safe and efficient electrical wiring.






