Have you ever wondered how your favorite movies and TV shows are shrunk down to fit on a tiny DVD, streamed over the internet, or even stored on your phone? It’s all thanks to incredible technology called video compression. Behind the scenes, a complex dance of algorithms works tirelessly to squeeze as much visual data as possible into a manageable file size, without sacrificing too much quality. Two dominant players in this world are H.264 and x264 – but what makes them different, and why should you care?
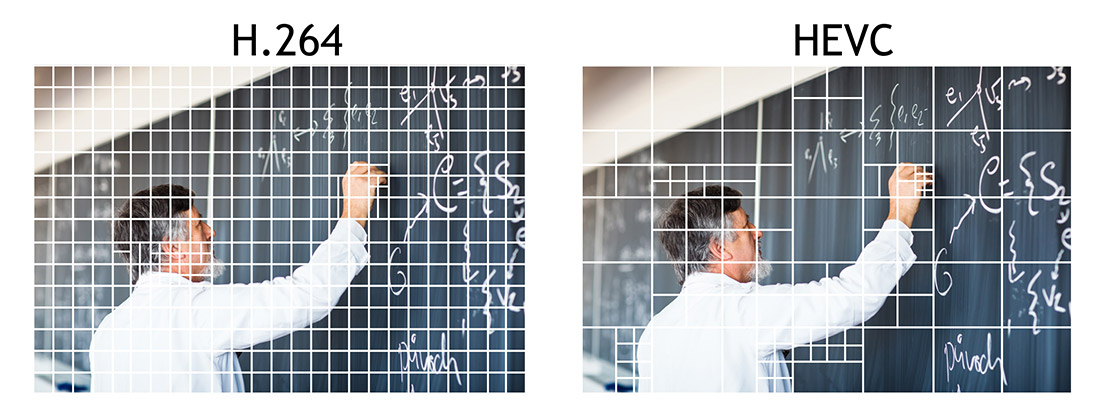

Image: www.brorsoft.cn
In the digital kingdom of video, H.264 reigns supreme. Officially known as **MPEG-4 Part 10** or **AVC (Advanced Video Coding)**, H.264 is a versatile standard that governs how video is compressed and decompressed. It’s the backbone of many popular video formats, from YouTube and Netflix to Blu-ray discs and video calls. x264, however, is a different beast. It’s a powerful open-source **software implementation** of the H.264 standard. Think of H.264 as the blueprint, and x264 as a skillful builder that translates those plans into a tangible, high-quality video experience.
H.264: The Industry Standard
A Glimpse into the Past:
The journey of H.264 began in the late 1990s, a collaborative effort between the **International Organization for Standardization (ISO)** and the **International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)**. The need for a more efficient video compression standard became apparent as digital video technologies surged in popularity. H.264, with its superior compression ratios, was the answer.
A Deep Dive into the Technology:
H.264 relies on a clever technique called **block-based coding**. Imagine dividing a video frame into small blocks, and then processing each block individually for compression. H.264 excels at identifying similarities between these blocks, removing redundancy, and representing the data more efficiently. Furthermore, **motion estimation and compensation** are employed to minimize the amount of information needed to encode movement in video. Think of it like comparing a sequence of still images – only the areas that change significantly are transmitted, saving valuable bandwidth.
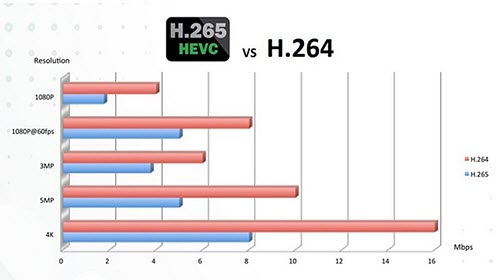
Image: walkerlonsind.blogspot.com
Defining the Advantages:
H.264 boasts numerous advantages that cemented its position as the industry standard:
- Superior compression efficiency: H.264 can achieve impressive compression ratios, resulting in smaller file sizes and reduced bandwidth requirements, making it ideal for streaming and downloading video content.
- Widely adopted: H.264 is embedded in countless devices and platforms, ensuring near-universal compatibility. Whether you’re watching a video on your phone, laptop, or smart TV, chances are high that H.264 is involved.
- Flexible and adaptable: H.264 is versatile enough to accommodate different video qualities, from standard definition to high definition and even 4K resolutions.
- Support for multiple profiles: H.264 offers flexibility based on specific needs. Different profiles define features like resolution, bitrate, and frame rate, allowing for optimized encoding for various applications.
x264: The Open-Source Alternative
A Free and Powerful Tool:
Unlike H.264, which is a standard, x264 is a specific implementation developed under the **GPL (GNU General Public License)**. This means that x264 is free to use and distribute, making it a popular choice for enthusiasts, researchers, and developers. But it’s not just about freedom – x264 packs a punch in terms of performance and quality.
Unleashing Performance and Advanced Features:
x264 is recognized for its exceptional compression efficiency. It employs advanced coding techniques and optimizations, often exceeding the compression capabilities of even the official H.264 implementations. x264 offers several advantages:
- High-quality encoding: x264 is known for its ability to produce visually impressive video at a given bitrate. This means you can enjoy better image clarity and detail compared to some other H.264 implementations.
- Wide range of options: x264 gives users a high level of control over encoding parameters, allowing them to fine-tune settings to match specific video content and playback environments.
- Active development: x264 is constantly being improved by a vibrant community of developers. New features and optimizations are introduced regularly, keeping it at the forefront of video compression technology.
H.264 vs. x264: A Head-to-Head Comparison
The Battle for Quality:
In terms of overall quality, x264 frequently edges out H.264 implementations. It offers more sophisticated encoding algorithms, allowing it to achieve a higher perceived quality at a given bitrate or file size. However, the quality gap isn’t always significant, and often depends on the specific H.264 encoder being used.
The Speed Factor:
When it comes to encoding speed, x264 is typically slower than commercial H.264 implementations. This is because x264 prioritizes quality over speed, employing more complex processing techniques. For time-sensitive tasks, a commercial H.264 encoder might be a better choice, but x264’s prowess in quality should not be ignored.
Considering the Ecosystem:
While x264 offers tremendous quality, it’s important to remember that it’s not as universally compatible as H.264. While the majority of devices and software support H.264 decoding, x264-encoded videos might require specific codecs or players for compatibility. For the broadest reach, H.264 remains the dominant choice.
The Future of Video Compression:
H.264 has been a cornerstone of video compression for over a decade, but the landscape is constantly evolving. New standards, such as **H.265 (HEVC)** and **AV1**, are emerging with even greater efficiency, offering further compression improvements and supporting higher resolutions like 8K. While H.264 still holds its ground, it’s important to acknowledge that the future of video compression lies in these newer technologies.
H264 Vs X264
Conclusion:
H.264 and x264 are both powerful tools in the world of video compression. H.264 reigns as a widely adopted industry standard, offering excellent compatibility and versatility. x264, on the other hand, provides a compelling open-source alternative with exceptional quality and advanced features. The choice between these two ultimately depends on your specific needs and priorities. Whether you’re encoding videos for professional use, sharing content online, or simply enjoying entertainment, understanding the distinctions between H.264 and x264 can empower you to make informed decisions. So, next time you encounter a video file, take a moment to appreciate the intricate workings of these technologies that have revolutionized our digital experience.






