Have you ever wondered about the subtle differences between “digital” and “electronic”? While they seem interchangeable in everyday conversations, there’s a distinct line that separates these two realms of technology. These terms, though often used interchangeably, describe fundamentally different concepts that shape our world. Understanding this distinction is crucial, as it allows us to navigate the ever-evolving landscape of information and technology with clarity and precision.
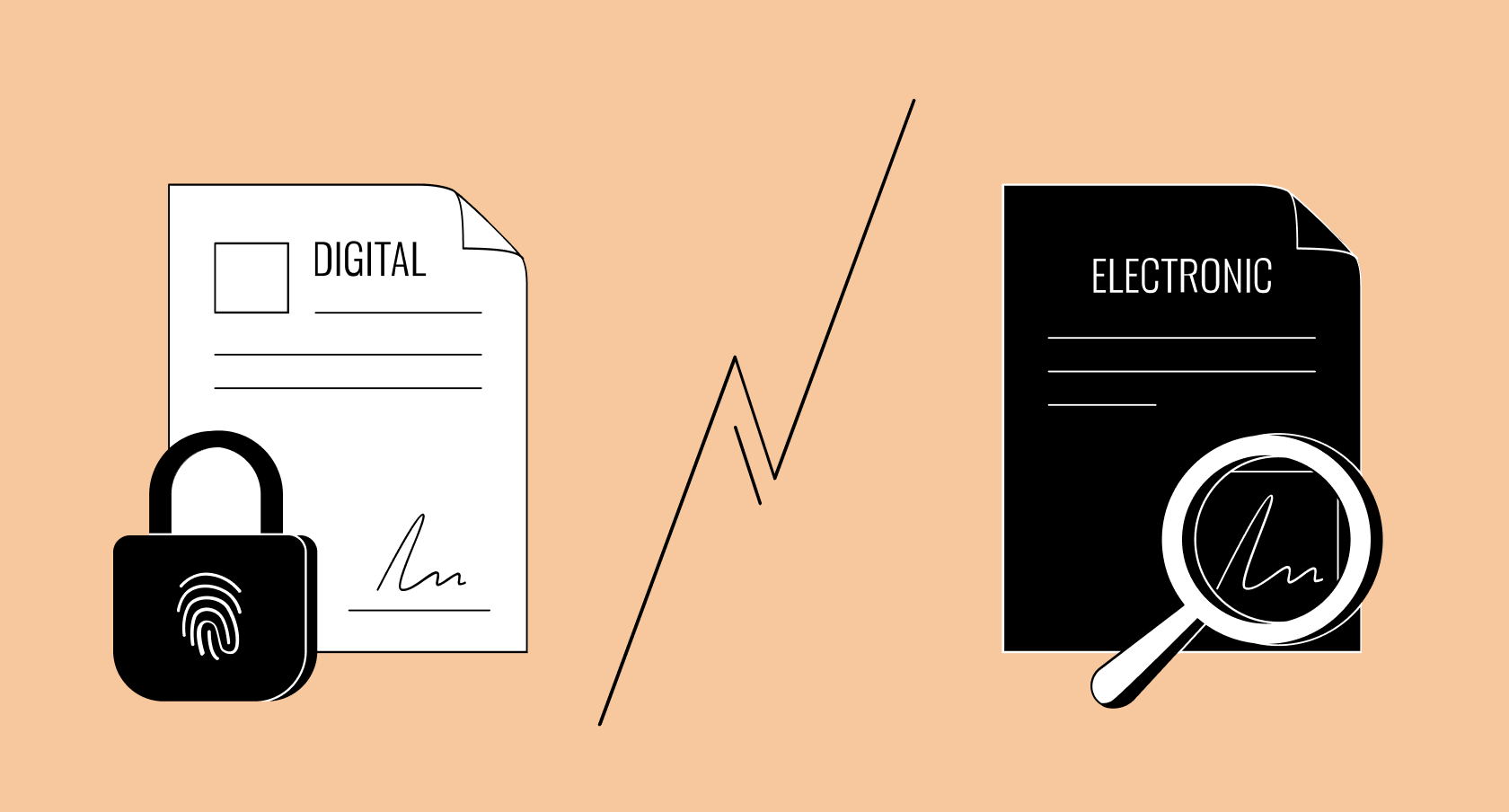
Image: digt.com
From the smartphones in our pockets to the internet connecting us globally, the “digital” and “electronic” have become integral parts of our lives. This article will explore the history, concepts, and applications of these distinct forms of technology. We’ll delve into the world of bits and bytes, circuits and signals, and uncover the fascinating relationship between the physical and digital worlds.
The Genesis of Electronic Technology: From Spark to Signals
The journey towards electronic technology began with the discovery of electricity. In the 18th century, scientists like Benjamin Franklin and Alessandro Volta paved the way by understanding the flow of electrons. This paved the path for the development of the first electronic devices, like the telegraph in 1837, which used electrical signals to transmit messages over long distances. This marked the dawn of a new era, where information was no longer bound by physical constraints. The invention of the radio in the late 19th century further expanded the reach of electronic communication, broadcasting sound waves through the air.
The invention of the vacuum tube in the early 20th century revolutionized electronics. These devices, capable of amplifying and controlling electrical signals, became the cornerstone of early radio, television, and computers. This period witnessed the rapid growth of electronic technology, enabling new forms of communication, entertainment, and computing.
Electronic technology essentially deals with the manipulation and transmission of electrical signals. It works by controlling the flow of electrons in various circuits and components. This technology encompasses a wide range of devices, from simple light bulbs to complex medical equipment, all operating based on the principles of electrical conductivity.
The Digital Revolution: From Analogue to Binary
While electronic technology laid the foundation, the advent of digital technology completely transformed our world. The concept of representing information using discrete units, called bits, revolutionized how we interact with technology. Instead of manipulating analog signals, digital technology utilizes binary code, a system of 0s and 1s, to represent data.
The development of the transistor in the mid-20th century was instrumental in the digital revolution. These tiny, semiconductor-based devices replaced bulky vacuum tubes, enabling the creation of smaller, more efficient, and affordable electronic devices. The invention of the integrated circuit, a miniature electronic circuit housed on a single chip, further propelled the miniaturization of technology and led to the development of personal computers and other digital devices.
The digital revolution brought significant advantages. Digital data is inherently more resistant to noise and distortion, making it more reliable for processing and transmission. Furthermore, its flexibility allows for the integration of different types of data, from text and images to audio and video. This paved the way for the development of the internet and the digital age we live in today.
Digital vs. Electronic: Key Differences
The distinction between “digital” and “electronic” lies in the way they represent and process information. Electronic devices operate based on continuous analog signals, where information is represented by varying levels of voltage or current. Digital devices, on the other hand, use discrete binary code, representing information as a series of 0s and 1s.
Think of a dimmer switch on a lamp as an example of analog technology. The brightness, controlled by the position of the switch, changes continuously. It represents the information (brightness) with an analog signal. In contrast, a light switch, with its two distinct states (on/off), represents the information digitally using a binary code (1 for on, 0 for off). This principle applies across various digital devices, including computers, smartphones, and other modern gadgets.
Here’s a table summarizing the key differences:
| Feature | Electronic | Digital |
|---|---|---|
| Information Representation | Analogue (continuous) | Binary (discrete) |
| Data Storage | Magnetic tapes, disks, etc. | Semiconductor memory, hard drives, etc. |
| Data Transmission | Analogue signals (e.g., radio waves) | Digital signals (e.g., optical fiber) |
| Noise Resistance | Less resistant | More resistant |
| Flexibility | Limited | High |
| Example | Television, Radio | Computer, Smartphone |
Image: www.brainkart.com
The Intertwined World of Digital and Electronic
Although seemingly distinct, digital and electronic technologies are deeply intertwined. Digital devices rely on electronic circuits to process information. The transistors, integrated circuits, and other electronic components form the physical foundation of digital technology. The transformation of data from the continuous analog world to the discrete digital realm is achieved through analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) and digital-to-analog converters (DACs). These specialized electronic components bridge the gap between the two.
Modern electronic devices, like smartphones and tablets, often combine both digital and electronic components. Electronic circuits power the display, speakers, and sensor functionalities, while digital processors handle complex tasks like processing data, running applications, and managing network connections.
Real-World Applications
The impact of digital and electronic technologies is pervasive in our daily lives. They have revolutionized communication, entertainment, healthcare, commerce, and countless other aspects of our society.
Communication: The internet, mobile phones, and social media have created a global network, connecting billions of people across continents. Digital communication has facilitated instant messaging, video calls, email, and the rapid exchange of information.
Entertainment: Digital technologies have transformed the entertainment industry, from streaming services and video games to digital music and virtual reality experiences. We now have access to a vast library of entertainment content at our fingertips.
Healthcare: Medical imaging technologies like MRI and CT scans rely on digital processing and electronic sensors to diagnose illnesses. Electronic health records (EHRs) streamline patient data management. Digital devices, such as wearable health trackers, monitor vital signs and provide insights into personal health.
The Future of Digital and Electronic Technology
The combination of digital and electronic technology is pushing the boundaries of innovation. The rise of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, robotics, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are shaping a future where devices are increasingly interconnected and intelligent.
The development of quantum computing holds the potential to revolutionize digital technology, enabling the processing of complex problems beyond the capabilities of today’s computers. Nanotechnologies are also expected to play a significant role, leading to smaller, faster, and more efficient electronic components.
Digital Vs Electronic
Conclusion
The digital and electronic technologies have come a long way, transforming our world in remarkable ways. While they may seem interchangeable, understanding their underlying principles and distinct characteristics provides a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of our technological world. As we navigate the future, the convergence of these technologies will continue to shape our lives, offering exciting possibilities for innovation and advancement.
Explore further! Visit online resources, read articles about AI, quantum computing, or the Internet of Things. Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below. Let’s continue to learn and explore the fascinating world of digital and electronic technologies.






