Have you ever stumbled upon the words “authentication” and “authentification” and felt a pang of confusion? Are you unsure which one is correct, or perhaps even if both are valid? You’re not alone. These two words, often used interchangeably, hold a subtle difference that can make a world of difference in the realm of security and identity verification. This article delves into the fascinating world of authentication vs. authentification, unraveling the mystery and shedding light on their unique roles in our digital lives.
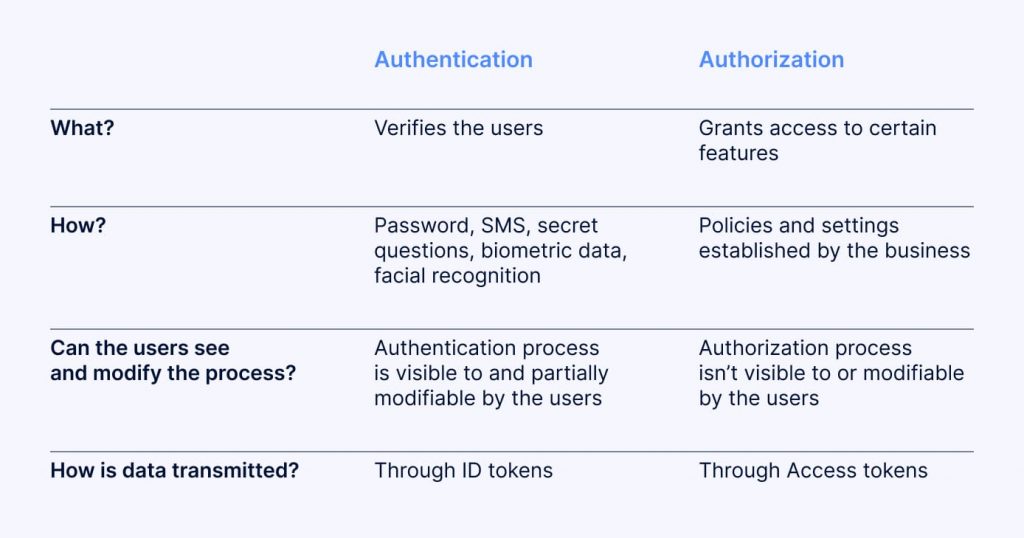
Image: sumsub.com
Authentication and authentification are often thrown around in the realm of cybersecurity, but their meanings and usage are often misunderstood. However, understanding the nuances between these two can help you navigate the complex world of digital security with more confidence. This article aims to debunk the myth surrounding these two terms, providing a clear explanation of their origins, functions, and how they differ in the realm of security and technology.
The Roots of Authentication
Before delving into the differences, it’s important to establish their common ground. Both “authentication” and “authentification” are derived from the Latin word “authenticus,” meaning “genuine” or “real.” This root underscores the core purpose of both concepts: verifying the genuineness of something or someone. However, the way in which they achieve this authenticity is where the difference lies.
Authentication: The Standard Bearer
Let’s start with the more common and widely accepted term: “authentication.” This word refers to the process of verifying a user’s identity to grant access to a system or resource. It’s the cornerstone of digital security, safeguarding our online accounts, financial transactions, and sensitive information. Think of it like a digital bouncer, ensuring only authorized individuals gain entry to the digital clubs we frequent.
How Authentication Works
Authentication relies on various methods to verify a user’s identity, often involving a combination of factors:
- Something you know: This might be a password, PIN, or secret question.
- Something you have: This could be a physical token, a smartcard, or a mobile device.
- Something you are: This involves biometric methods such as fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, or iris scanning.

Image: www.secureauth.com
Types of Authentication
Authentication manifests itself in various forms, each tailored to different contexts and security needs:
- Password-based authentication: The most common method, relying on a secret password known only to the user.
- Two-factor authentication (2FA): Combines multiple authentication factors, often requiring a password and a code sent to a mobile device, for stronger security.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA): Goes beyond two factors, incorporating additional layers of verification for highly sensitive systems.
- Biometric authentication: Utilizes unique biological characteristics for identification.
- Certificate-based authentication: Employs digital certificates to verify the authenticity of both the user and the system.
Authentification: A Less Frequent Player
While “authentication” reigns supreme, “authentification” also holds a place in the English language, albeit a less prominent one. The Oxford English Dictionary defines “authentification” as “the act of authenticating something.” In other words, it signifies the process of making something authentic, rather than verifying its authenticity. The most common usage of “authentification” is in legal contexts, where it refers to the process of proving that a document is genuine and not forged.
Authentification in Legal Matters
In legal settings, “authentification” takes center stage when dealing with documents, evidence, and other legal materials. It’s a crucial process for establishing the validity and reliability of legal documentation. This process often involves:
- Notarization: A certified official verifies the identity of the signer and the document’s authenticity.
- Witnessing: Individuals attest to the genuineness of the document and the signature.
- Chain of custody: Ensuring the document remains untampered and in secure possession from its creation to its use.
The Battle of the Words: A Matter of Precision
While both words share a common origin and revolve around establishing authenticity, their distinct meanings and usage shouldn’t be overlooked. “Authentication” is the more prevalent term, widely adopted in the world of technology and online security. “Authentification,” though less common, holds its ground in legal contexts, highlighting the process of ensuring the genuineness of legal documents and evidence.
Choosing the Right Word: The Importance of Context
When navigating the complexities of digital security and legal matters, choosing the right word is crucial for effective communication and understanding. You can make a decisive choice by factoring in the context of the situation.
- If you’re discussing the process of verifying someone’s identity to grant access to a system, “authentication” is the more fitting choice.
- If you’re examining the process of establishing the legitimacy of a document in a legal setting, “authentification” would be the appropriate term.
A World of Authentication: Beyond the Digital Doors
The importance of authentication isn’t confined to the digital realm. Even in our physical world, authentication plays a vital role, ensuring security and access:
- Driver’s licenses: Government-issued documents that authenticate our identity and driving privileges.
- Passports: Travel documents used to authenticate our nationality and permit international travel.
- Identification cards: Used to verify our identity in various settings, from workplaces to events.
The Future of Authentication: A Journey into the Unknown
The world of authentication is continuously evolving, adapting to emerging technologies and evolving security threats.
- Biometric Authentication: This technology is gaining traction, utilizing our unique biological features for stronger and more convenient authentication. Think fingerprint scanners, facial recognition, and voice recognition.
- Quantum-resistant cryptography: As quantum computing advances, new forms of cryptography are emerging to withstand attacks from powerful quantum computers, further enhancing the security of authentication methods.
- Zero-trust security: This approach assumes no user or device can be trusted by default, requiring authentication for every interaction, creating a more secure environment.
Authentication Vs Authentification
Conclusion: The Authentic Truth
Authentication and authentification, though often interchanged, hold distinct meanings and applications. Understanding these nuances is critical for effectively navigating the complexities of digital security and legal matters. With the internet becoming an integral part of our lives, safeguarding our privacy and sensitive information is more vital than ever. Authentication stands as a cornerstone of this endeavor, continually evolving and adapting to the ever-shifting landscape of digital security. So, the next time you encounter these two terms, remember their distinct roles and choose wisely to ensure clarity and accuracy in your discussions.






