Picture this: you’re about to plug in your phone charger, and for a moment, you pause. You see two wires, one is white, and one is black. A fleeting thought crosses your mind – which one is the “hot” wire? This simple question leads us into the fascinating world of electricity, where understanding the difference between hot and load wires is not just about curiosity, but also safety.

Image: electrouniversity.com
We use electricity every day, from powering our homes and appliances to connecting with the digital world. However, the intricate network of wires and circuits behind these conveniences can feel like a hidden world, shrouded in mystery. One essential element in understanding this hidden world is the distinction between hot and load wires. The hot wire, often denoted by black or red insulation, carries the electrical current from the source, while the load wire, typically white or gray, acts as the return path. Delving into this seemingly simple difference reveals a complex tapestry of electrical safety, functionality, and even history.
The Electrifying History of Hot and Load
To truly grasp the concept of hot and load wires, we must step back in time, to the dawn of electricity. Imagine the early electrical systems of the late 19th century – a time when the very concept of current flow was still being explored. Thomas Edison, a pioneer in the field, used a direct current (DC) system, where electricity flowed in a single direction. In his system, the “hot” wire was the positive terminal, and the “ground” wire was the negative terminal.
However, as electrical systems evolved, alternating current (AC) became the standard. In AC systems, the direction of current flow changes periodically, making the concept of a “positive” or “negative” terminal more fluid. As a consequence, the electrical code evolved, and the concept of a “neutral” wire emerged. This “neutral” wire essentially became the return path for the current, carrying it back to the source, while the “hot” wire remained the path for the incoming current.
Delving Deeper: The Hot Wire & Its Role
The hot wire is the conductor that carries the current from the electrical source, often a power plant or a generator. It’s typically insulated with black or red colors for easy identification. Think of the hot wire as the lifeline of electricity, the main artery delivering power to your appliances, lights, and other devices.
The hot wire, carrying the “live” current, holds a significant potential energy. This is why it’s crucial to handle the hot wire with extreme caution. Accidental contact can result in a severe electric shock, potentially leading to serious injuries or even death.
The Unsung Hero: The Load Wire & Its Journey
The load wire, often insulated in white or gray, works in concert with the hot wire to create the complete circuit. It acts as the return path for the current, transporting it back to the source after it has powered the load. This load can be anything – your refrigerator, your smartphone charger, or even a light bulb.
Imagine the load wire as the return route, a highway channeling the current back to its origin. Without the load wire, the current would have nowhere to go, effectively halting the flow of electricity and rendering your devices unusable.
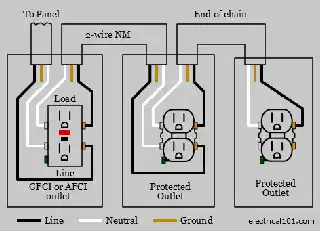
Image: www.m.electrical101.com
Grounding: The Safety Net of the Electrical System
While the hot and load wires are essential for delivering and returning the electrical current, there’s a third crucial component: the ground wire. Typically insulated in green or bare copper, the ground wire is a safety mechanism, providing an alternative path for the current in case of a fault.
In a nutshell, the ground wire acts as a safety net, preventing a potentially dangerous scenario. If a malfunction occurs, such as a faulty appliance, the ground wire provides a low-resistance path for the current to flow to the earth, preventing electrical shock and potential fire hazards.
Hot vs Load Wire: The Practical Implications
Understanding the difference between hot and load wires is not just an academic exercise. It’s a necessity for anyone handling electrical devices, especially when working on DIY projects around the house.
Here are some common scenarios where knowing the distinction between hot and load wires is crucial:
- Electrical Wiring: When installing new electrical outlets or wiring devices, it’s vital to correctly identify and connect the hot, load, and ground wires according to the established electrical code.
- Electrical Repairs: When troubleshooting electrical issues, the ability to differentiate between hot and load wires can save time, prevent damage, and ensure safety.
- Home Appliances: It’s important to be aware of the wiring configurations of home appliances to ensure proper operation and safety.
Expert Insights & Actionable Tips: Navigating the Electrical World
Seeking advice from a qualified electrician is crucial when working with electrical systems. Here are some tips for navigating the electrical world:
- Always Turn Off Power: Before working with any electrical wiring or devices, always turn off the power to the circuit at the breaker box.
- Use Proper Tools: Use insulated screwdrivers and other tools specifically designed for electrical work.
- Check for Insulation: Inspect wires for any signs of damage or fraying insulation. Damaged insulation can lead to electrical shocks or fires.
Hot Vs Load Wire
A Final Word on the Power of Knowledge
Understanding the intricacies of hot and load wires empowers you with the knowledge and awareness necessary to handle electrical situations safely. While seemingly complex, the concepts behind this fundamental electrical distinction are relatively simple.
By understanding the role of each wire- the hot wire, the load wire, and the critical ground wire- you can navigate the electrical world with greater caution and confidence. Remember, electricity is a powerful force, and by respecting it and understanding its fundamental principles, we can effectively use this vital resource to power our lives and shape our future.






