Ever wondered why some light bulbs seem to radiate a brighter, more intense glow than others? The answer lies in the wattage, a measure of power that determines how much energy a device consumes. While you might be familiar with 60-watt bulbs, the rise of energy-efficient lighting has introduced the 100-watt option, sparking questions about their differences and which one reigns supreme.

Image: www.ledlightexpert.com
This exploration delves into the world of wattage, comparing the illuminating power of 100-watt and 60-watt bulbs. We’ll unravel their historical context, analyze their pros and cons, and explore the ongoing trends that are shaping the future of lighting. By the end of this journey, you’ll possess a comprehensive understanding of these two wattage classes and be empowered to make informed choices about your lighting needs.
The Genesis of Watt: A Historical Perspective
The concept of wattage, named after Scottish inventor James Watt, traces its roots to the 18th century. Watt, renowned for his improvements to the steam engine, laid the foundation for understanding power as a measure of energy consumption over time.
In the realm of lighting, the incandescent bulb, invented by Thomas Edison in 1879, ushered in the era of electric illumination. The wattage of an incandescent bulb directly reflects its power consumption and, consequently, its brightness. Early bulbs were generally low wattage, with 60 watts becoming a standard choice for residential use. This was primarily because these early bulbs were less efficient, converting a significant portion of their energy into heat rather than light.
Understanding the Basics: Power and Brightness
Watts (W) represent the rate at which energy is consumed. A higher wattage signifies a device’s increased energy consumption, resulting in a heightened output. In the case of light bulbs, this output manifests as increased brightness.
To illustrate the relationship between wattage and brightness, imagine two light bulbs: a 60-watt bulb and a 100-watt bulb. The 100-watt bulb consumes more energy, which translates into a brighter glow. The exact amount of brightness, however, goes beyond just wattage and depends on factors like the bulb’s efficiency and type.
100-watt vs. 60-watt: A Side-by-Side Comparison
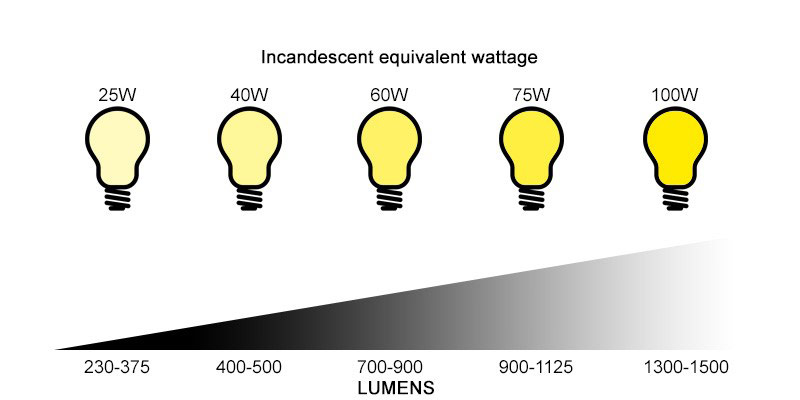
Image: www.lamps-on-line.com
Brightness: The Obvious Difference
The most noticeable difference between a 100-watt and a 60-watt bulb lies in their brightness. As mentioned earlier, the 100-watt bulb will consistently produce a brighter light than its 60-watt counterpart. This brightness difference can be significant, particularly when considering larger spaces or tasks requiring enhanced visibility.
Energy Consumption: A Trade-off
While the 100-watt bulb provides a brighter output, it also consumes more energy. This translates into higher electricity bills. As energy conservation becomes increasingly important, the higher wattage of the 100-watt bulb often makes it less appealing for environmentally conscious consumers.
Cost: A Factor to Ponder
Generally, 100-watt bulbs have a higher purchase price compared to 60-watt bulbs. This price difference can be attributed to their manufacturing costs, which are often influenced by the materials used and the bulb’s design.
Lifespan: A Variable Aspect
The lifespan of a light bulb—the number of hours it can operate before failing—is a crucial factor for many consumers. The lifespan of both 60-watt and 100-watt incandescent bulbs can vary depending on specific factors like the bulb’s quality and usage patterns. However, in general, incandescent bulbs with higher wattage tend to have shorter lifespans.
It’s important to note that the lifespans of incandescent bulbs have been largely overshadowed by the advent of energy-efficient alternatives. These alternatives, such as LED and CFL bulbs, boast significantly longer lifespans, rendering the traditional comparison between 60-watt and 100-watt incandescent bulbs less relevant in modern contexts.
The Evolution of Lighting: A Shift Towards Efficiency
The comparison between 100-watt and 60-watt incandescent bulbs is a historical snapshot, a testament to a technology that is increasingly being replaced by more efficient options. As we move towards a future driven by sustainability, the focus shifts from wattage to lumens, a measure of light output that offers a more accurate comparison of brightness across different bulb types.
LEDs: The New Standard
LED (Light Emitting Diode) bulbs have taken the lighting world by storm. They are incredibly energy-efficient, converting a higher percentage of energy into light compared to their incandescent counterparts. This results in brighter illumination with significantly lower energy consumption.
CFLs: A Step in the Right Direction
CFL (Compact Fluorescent Lamp) bulbs, while not as efficient as LEDs, offer a more energy-efficient alternative to incandescent bulbs. Their spiral shape allows for a more compact design compared to traditional fluorescent tubes, making them suitable for standard light fixtures.
Choosing the Right Lighting: Considerations and Recommendations
While the 100-watt vs. 60-watt debate has largely been overtaken by the evolution of lighting technology, understanding these wattage classes provides a foundation for navigating the modern lighting landscape. When choosing bulbs, consider the following factors:
- Brightness: Determine the required level of brightness for your space or task. Refer to lumens, a unit that measures light output, for a more accurate comparison across bulb types.
- Energy efficiency: Select bulbs with a high Energy Star rating, denoting energy-efficient performance.
- Lifespan: Opt for bulbs with longer lifespans, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing waste.
- Color temperature: Consider the desired color temperature, measured in Kelvin, for the ambiance you want to create. Warmer colors (like soft whites) create a cozy atmosphere, while cooler colors (like bright whites) provide a more stimulating environment.
100w Vs 60w
Making Informed Decisions: The Future of Lighting
The world of lighting is constantly evolving. As energy efficiency and technological advancements continue to drive innovation, we can expect to see even brighter, more sustainable lighting solutions emerge. By understanding the basics of wattage and the broader context of lighting technology, consumers can make informed choices that align with their lighting needs and environmental considerations.
So the next time you’re facing the dilemma of choosing between a 100-watt and a 60-watt bulb, remember that the world of lighting has expanded. Embracing energy-efficient alternatives like LEDs and CFLs will not only contribute to a greener future but also provide a brighter, more illuminating experience.






