Imagine a world without the vibrant blue oceans, majestic mountains, or fertile green valleys that we cherish. It’s hard to fathom, isn’t it? This is the world of Earth Science, a fascinating journey into the heart of our planet and its dynamic processes that shape our very existence. Earth Science Unit 1 lays the foundation for this exploration, introducing the fundamental concepts that govern our planet’s structure, composition, and interactions with the universe.
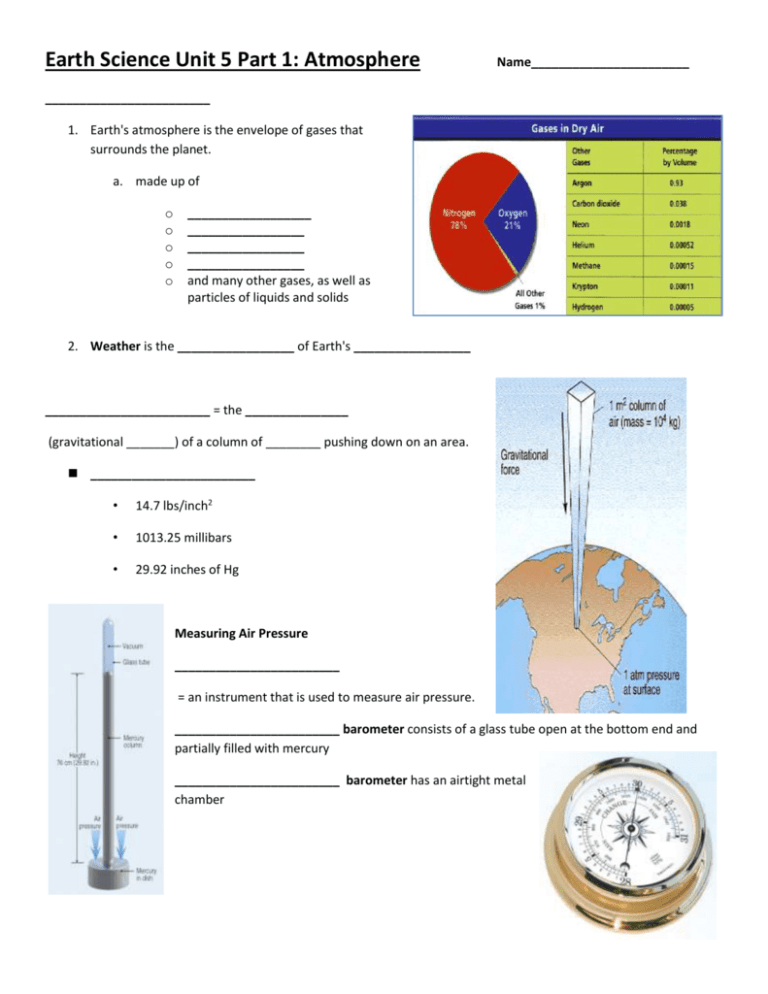
Image: studylib.net
This unit is more than just a collection of facts; it’s a doorway to understanding the interconnectedness of all things. From the scorching heat of the Earth’s core to the delicate balance of the atmosphere, we’ll delve into the intricate web of processes that influence our daily lives and future prospects. Whether you’re a student eager to unravel the secrets of our planet, or simply someone with a curious mind, this exploration promises to be both eye-opening and intellectually stimulating.
Unveiling the Earth’s Structure: From Core to Crust
Similar to a perfectly layered cake, the Earth boasts a captivating inner structure. This structure is best understood through a journey from its fiery core to its outermost layer, the crust. Let’s embark on this fascinating descent:
1. The Earth’s Core: A Fiery Heart
Deep within the Earth’s embrace lies the core, a sphere of immense heat and pressure. This region is predominantly composed of iron and nickel, and is subdivided into two parts: the solid inner core and the liquid outer core. The inner core is a solid ball of metal, subjected to immense pressure that prevents it from melting, despite its extreme temperature. The outer core, on the other hand, is molten, churning and creating electric currents that generate the Earth’s magnetic field – a shield that protects us from harmful solar radiation.
2. The Mantle: A Viscous Layer
Surrounding the core is the mantle, a thick, viscous layer that constitutes about 84% of the Earth’s volume. This layer is composed of silicate minerals and behaves like a tremendously thick fluid. The mantle is not static; it’s in constant motion due to convection currents driven by heat from the core. These currents are responsible for the movement of tectonic plates, a process that shapes continents, forms mountains, and creates earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.

Image: www.teacherspayteachers.com
3. The Crust: Our Fragile Surface
The outermost layer of the Earth is the crust, a relatively thin, rigid layer that comprises both oceanic crust (found beneath the oceans) and continental crust (forming the continents). The oceanic crust is denser and thinner than the continental crust. This difference in density plays a crucial role in plate tectonics, where denser oceanic plates tend to subduct under lighter continental plates, creating volcanic arcs and mountain ranges.
Unveiling the Earth’s Systems: Interplay of Forces
Earth science is not merely about understanding the Earth’s structure, but also about recognizing the intricate interplay of its various systems. These systems are complex, interconnected, and work together to shape the unique environment we inhabit.
1. The Atmosphere: Our Protective Blanket
The Earth’s atmosphere is a vibrant blanket of gases that surrounds our planet, providing essential life support. This blanket is primarily composed of nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), and other trace gases. The atmosphere plays a crucial role in regulating our planet’s temperature, shielding us from harmful solar radiation, and facilitating weather patterns.
2. The Hydrosphere: The Life-Giving Waters
Water, the essence of life, is distributed throughout our planet in various forms, constituting the hydrosphere. This includes oceans, lakes, rivers, groundwater, and even the water vapor in the atmosphere. The hydrosphere plays a vital role in regulating Earth’s climate, shaping landforms through erosion and deposition, and supporting the diverse ecosystems that thrive on our planet.
3. The Biosphere: The Canvas of Life
The biosphere encompasses all living organisms, from the smallest bacteria to the largest whales, interacting within the Earth’s systems. This web of life is interconnected, with organisms influencing and adapting to their environment, and in turn shaping the planet’s composition and processes. From the microbe communities in the soil to the vast forests that oxygenate our atmosphere, the biosphere plays an integral role in maintaining the delicate balance of our planet.
4. The Geosphere: A Dynamic Interior
The Earth’s geosphere refers to the solid, non-living components of our planet, including rocks, minerals, and soil. This system is constantly changing due to the internal dynamics of the Earth, including plate tectonics, volcanic activity, and erosion. The geosphere provides the foundation for all other Earth systems, delivering the minerals, rocks, and soil that sustain life and shape our landscapes.
Earth Science Unit 1
Earth Science Unit 1: A Foundation for Exploration
Earth Science Unit 1 lays the bedrock for understanding the complex and fascinating world we inhabit. It introduces us to the remarkable structure of our planet, the intricate interplay of its systems, and the incredible processes that sculpt our landscapes and influence our lives. This unit is not just about memorizing facts; it’s about igniting a passion for discovery, fostering a sense of awe for the wonders of our planet, and empowering us to make informed decisions about our impact on this precious and fragile Earth.
As you delve deeper into the world of Earth Science, you’ll discover a wealth of resources and opportunities for further exploration. Don’t hesitate to expand your knowledge, engage in discussions with fellow learners, and share your newfound understanding to inspire others. In the words of renowned scientist, Carl Sagan, “We are all connected, to each other, to the Earth, to the cosmos. We are all stardust.”






