Have you ever wondered why certain social practices or institutions exist? Do you ever feel puzzled by the underlying reasons behind familiar traditions, rules, or social norms? You’re not alone. Understanding the motivations and consequences behind these aspects of our lives is crucial to comprehending the very fabric of society. This is where the concept of manifest functions comes in—it’s a sociological lens that helps us decipher the overt, intended purposes of social phenomena.
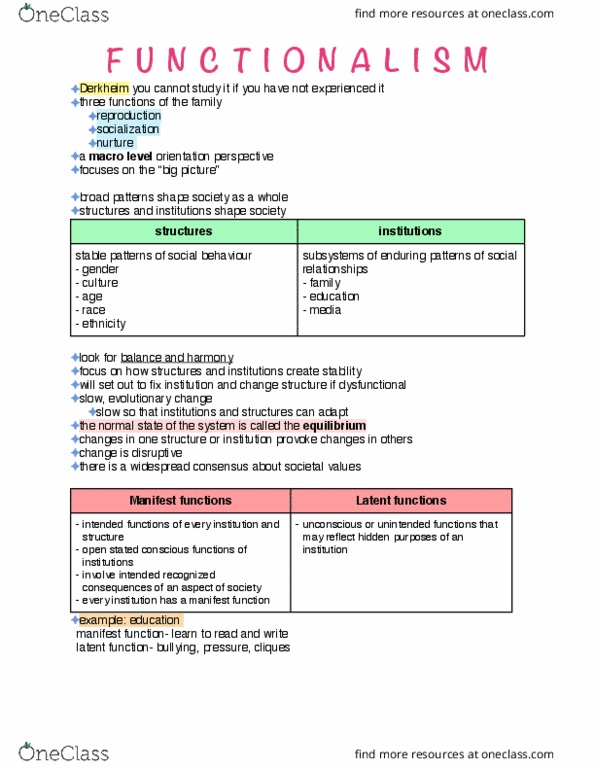
Image: www.mypromosource.com.au
But before we dive into the heart of the matter, imagine attending a bustling farmers market. You see vibrant vegetables, local crafts, and friendly interactions. The market’s manifest function is undeniably clear: it’s a place for people to purchase fresh produce and support local artisans. Yet, what if there is more than meets the eye? What if this vibrant space also fosters community spirit, creates economic opportunities for local businesses, and encourages healthy eating habits? These deeper, unintended consequences are known as latent functions—and they’re just as essential to unraveling the complexities of social life.
Understanding Manifest Functions: The Key to Social Order
To truly grasp the concept of manifest functions, we need to delve into the field of sociology. Sociologists, like detectives with a keen eye for patterns and motives, strive to understand the intricate workings of human interactions within society. They examine the forces that shape our lives, from the family dynamics to the global economy. And in their quest for understanding, they employ frameworks like the functionalist perspective, which views society as a complex system with interconnected parts.
One of the central tenets of this perspective is the idea that each social institution—be it the family, education, religion, or government—possesses a function—a contribution it makes to the overall stability and well-being of society. And within these functions, we uncover two distinct categories: the manifest and latent.
Imagine a classroom, filled with students eagerly absorbing knowledge. The manifest function of education is undeniably straightforward: to impart skills, knowledge, and values to students, preparing them for future careers and roles in society. But what about the latent functions that operate beneath the surface? Education can be a powerful tool for social integration, promoting cultural transmission, and fostering social connections among students from diverse backgrounds. It can also contribute to social control, as schools instill values and norms that maintain social order.
Beyond the Surface: Unmasking the Hidden Purposes
As we examine the manifest functions of various social institutions, patterns emerge. Let’s take the example of religion. Its manifest function is often seen as providing spiritual guidance, moral principles, and a sense of community. Religious practices and beliefs can offer comfort in times of hardship and provide a framework for meaning and purpose in life. But the latent functions run deeper, influencing social solidarity by fostering a shared sense of identity and belonging. Religions can also play a role in social control, reinforcing societal norms and expectations.
Delving into the manifest functions of the healthcare system, we find its primary goal is to maintain and improve the well-being of individuals and communities. Health services aim to prevent and treat diseases, provide medical care, and promote healthy lifestyles. Yet, the latent functions of this system can extend beyond these immediate objectives. The healthcare system can act as a social safety net, providing essential services to vulnerable populations. It can also contribute to economic development by generating jobs and supporting research.
Unveiling the Dynamics of Change: Manifest and Latent Functions in Action
The concept of manifest functions is a powerful tool for analyzing the dynamics of change in society. As societies evolve, the roles and functions of institutions often shift. Consider the changing manifest functions of the family unit. Traditionally, families were primarily responsible for economic production, education, and socialization. However, as societies have become more industrialized and complex, the family’s role has evolved, with more emphasis placed on providing emotional support and nurturing personal growth.
Simultaneously, the latent functions of the family have also shifted. In the past, families played a significant role in maintaining social order through traditional norms and expectations. Yet, in contemporary societies, families are grappling with changing gender roles, increasing diversity, and the impact of globalization. These shifts in the family structure not only alter the manifest functions but also reshape the latent functions of this cornerstone of society.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-493189993-5811b8f95f9b58564c341106.jpg)
Image: www.thoughtco.com
Empowering Yourself with the Lens of Manifest Functions
Understanding the manifest functions of social institutions isn’t just an academic exercise—it holds practical implications for our everyday lives. By recognizing the intended purposes and the underlying mechanisms that drive various social activities, we gain a deeper understanding of how our own actions and decisions contribute to the larger tapestry of society.
The insights gained from examining manifest functions can empower us to become more informed citizens, engaging in thoughtful discourse and contributing to positive change. By analyzing the manifest functions of governmental institutions, we can better understand how policies and regulations impact our lives. We can become more active participants in shaping the future of our communities and advocating for policies that align with our values.
What Is A Manifest Function
Beyond the Textbook: Applying Knowledge to Real Life
Beyond the realm of politics, the knowledge of manifest functions can be applied to various aspects of our personal lives. As we navigate relationships, build careers, and participate in communities, we can use this framework to gain clarity on the intended goals and unintended consequences of our actions. We can become more mindful of how our choices impact others and contribute to the social fabric.
For example, when choosing a career, we can analyze the manifest function – the intended purpose. Is it to earn a living, contribute to society, or fulfill a personal passion? By digging deeper, we can also consider the latent functions – the social and personal impact of our career choice on our relationships, lifestyle, and overall well-being.
Ultimately, understanding the manifest functions of social phenomena empowers us to become more critical thinkers, active participants in shaping our world, and informed individuals navigating the complexities of social life. By shedding light on the intended purposes and hidden motivations behind the institutions and practices that surround us, we gain a clearer picture of the forces shaping our lives and the roles we play in the grand scheme of society.
In conclusion, the concept of manifest functions is a potent tool for understanding the complexities of society. It prompts us to think beyond the surface, uncovering the intended purposes and unintended consequences of social institutions and practices. By grasping this key concept, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate dynamics of the social world, becoming more informed citizens and navigating the complexities of life with greater awareness and insight.






