Imagine a young child, barely able to speak, mimicking their parents’ every action – the way they hold a fork, the words they use, the way they greet others. This seemingly effortless imitation is the foundation of socialization, a complex process that shapes our deepest values, beliefs, and behaviors. But what are the forces behind this transformation? They are what we call agents of socialization, the individuals and institutions that mold us into the people we become.

Image: www.slideshare.net
We all know about our parents, teachers, and friends, but the influence of socialization extends far beyond these familiar figures. From the media we consume to the laws that govern our society, countless agents are constantly shaping our worldview. Understanding these invisible hands is crucial to understanding ourselves, our interactions with others, and the very fabric of society itself.
Unraveling the Threads of Socialization: A Deep Dive
Socialization, put simply, is the process through which individuals learn the norms, values, and behaviors of their society. It’s a lifelong journey that begins at birth and continues throughout our lives. Agents of socialization are the crucial actors in this journey, transmitting cultural knowledge and shaping our understanding of the world.
The Primary Agents: Family
The family is often considered the first and most influential agent of socialization. Parents, siblings, and extended family members provide a child’s initial social environment, teaching them basic skills, instilling values, and fostering a sense of belonging. From learning to speak and eat to understanding right and wrong, the family lays the foundation for a child’s social development.
- Early Childhood: Parents are the primary source of language, social skills, and emotional regulation. They teach children about hygiene, manners, and appropriate behavior.
- Later Childhood and Adolescence: Family relationships continue to shape a child’s self-esteem, identity, and views on relationships.
- Beyond Childhood: Even into adulthood, the family remains a powerful influence on our beliefs, values, and decision-making.
The Educational Architect: School
Beyond the home, school plays a critical role in socializing children. It’s a microcosm of society where students learn not only academic subjects but also social norms, rules, and expectations.
- Explicit Instruction: Teachers directly instruct students on values like honesty, fairness, and responsibility.
- Social Interaction: School provides a social environment where children learn to interact with their peers, resolve conflicts, and develop social skills.
- Hidden Curriculum: Schools also transmit unspoken messages through the structure of the institution itself. For example, the emphasis on punctuality, obedience, and competition can shape students’ perceptions of success and achievement.
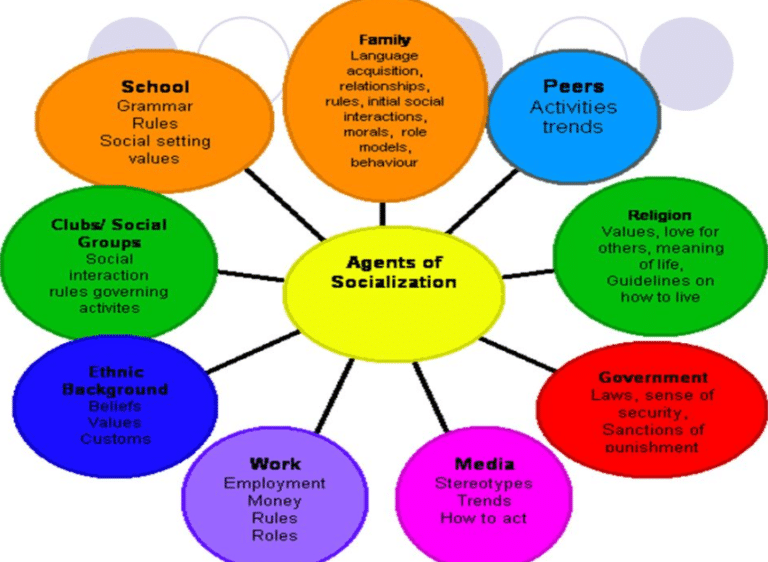
Image: educationisaround.com
The Mirror of Society: Peer Groups
As children grow older, peer groups become increasingly influential. These social circles provide a sense of belonging, approval, and acceptance.
- Social Identity: Peer groups contribute to the development of a child’s self-image and social identity.
- Norm Construction: Peers can reinforce societal norms or challenge them, promoting rebellious or conforming behaviors.
- Social Skills Development: Interactions with peers teach valuable social skills like cooperation, negotiation, and conflict resolution.
The Shaping Influence of Media
In today’s digital age, media has become a pervasive agent of socialization. From television shows and movies to social media platforms and online news sources, media constantly bombards us with messages, shaping our beliefs, values, and perspectives on the world.
- Entertainment and Escapism: Media can offer entertainment and escapism, but it also subtly influences our perceptions of gender roles, race, social status, and other aspects of society.
- News and Information: The news media shapes our understanding of current events, influencing our political views and social attitudes.
- Social Media: Social media platforms create online communities and influence trends, shaping our perceptions of what’s “cool” or “normal.”
Other Key Agents
Beyond the primary agents, several other forces contribute to socialization:
- Religious Institutions: Religion often provides moral guidelines, ethical frameworks, and a sense of community.
- Government and Legal Systems: Laws and policies shape our behavior, promoting order and influencing our values.
- Workplace: The workplace teaches us specific skills and work-related norms, shaping our professional identity.
- Culture: Shared beliefs, values, and practices of a society influence our thinking and behavior.
Navigating the Maze of Socialization: Insights and Actionable Tips
Recognizing the role of agents of socialization is essential for understanding ourselves and our place in society. It allows us to critically examine the influences that shape our beliefs and behaviors, fostering conscious awareness and a more nuanced perspective.
- Become an Informed Consumer of Media: Be mindful of the messages you receive from various media sources. Question the information you encounter and seek diverse perspectives.
- Promote Critical Thinking in Everyday Life: Challenge your own assumptions and biases. Ask yourself how your upbringing, school experiences, or social circles have shaped your views.
- Embrace Diversity and Inclusion: Engage with people from different backgrounds, cultures, and perspectives. Expand your horizons and challenge your own biases.
Definition Of Agents Of Socialization
Embracing the Journey
The process of socialization is a constant journey, a dynamic interplay of influences that shape who we are and how we interact with the world. By understanding the agents that play a role in this journey, we can engage with the world more consciously, make informed choices, and contribute to a more just and inclusive society.






