Remember that awkward first day of high school? You were thrown into a new environment, trying to decode the unspoken rules of social interaction. Suddenly, you were acutely aware of things like fashion trends, popular cliques, and even the nuanced language of the hallways. That experience, however uncomfortable, was a microcosm of the central themes explored in Chapter 2 of your sociology textbook – the foundations of social interaction and the very building blocks of society.
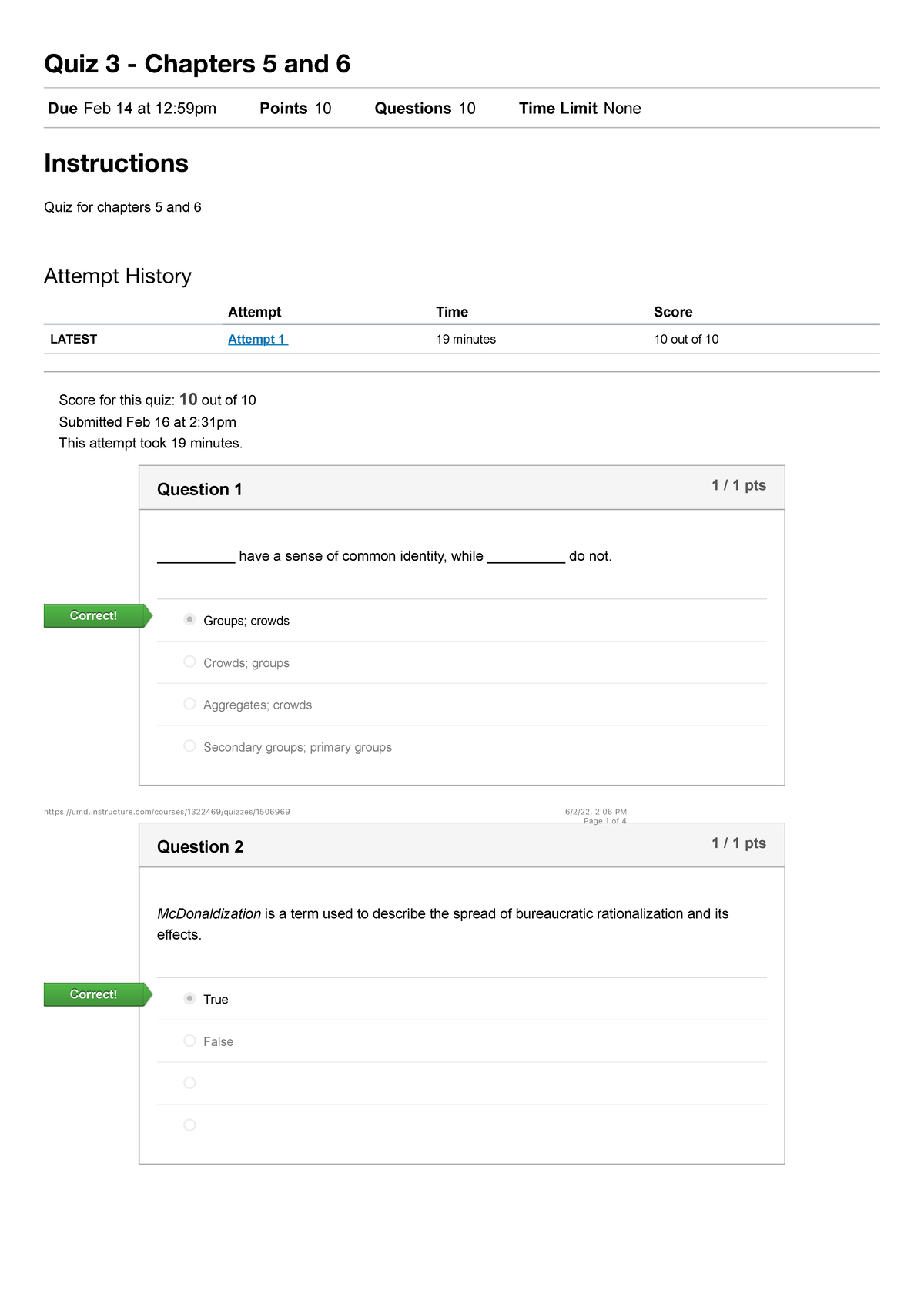
Image: www.studocu.com
This chapter, while seemingly basic, is crucial for understanding the complexities of human behavior and social structures. It helps us unravel the invisible threads that connect us, influence our decisions, and shape our world.
Understanding the Building Blocks of Society: Social Interaction and Culture
Social Interaction: The Dance of Human Connection
Social interaction is the foundation upon which all of society rests. It is the process by which individuals shape, interpret, and respond to one another’s actions, creating a tapestry of shared meanings and expectations. Imagine a simple conversation: the words exchanged, the gestures used, the subtle shifts in tone – all these elements contribute to the ongoing dance of social interaction.
Chapter 2 likely delves into key concepts like:
- Social Norms: The unwritten rules that guide our behavior in society. These range from the seemingly obvious (like waiting your turn) to the more subtle (like maintaining eye contact during a conversation.)
- Status and Roles: The positions we occupy in society and the expected behavior associated with them. From being a student to a parent, each role carries a set of norms that influences how we act and how others perceive us.
- Social Groups: The collective units that shape our identities and provide us with a sense of belonging. These can be immediate (like a family) or more expansive (like a religious group).
Culture: The Lens Through Which We View the World
Culture, in its broadest sense, is the shared learned behaviors, beliefs, attitudes, values, and material objects that characterize a society. It’s the lens through which we interpret the world around us and it profoundly influences our social interactions. Culture can be seen in everything from our language and traditions to our fashion choices and cuisine.
Key concepts within this realm include:
- Material Culture: The physical objects that are created and used by a society (e.g., technology, art, architecture.)
- Nonmaterial Culture: The intangible aspects of culture, including beliefs, values, norms, and language.
- Cultural Diversity: The vast array of cultures that exist around the world, highlighting the vibrant tapestry of human expression.

Image: www.coursehero.com
Why Chapter 2 Matters: Building a Stronger Foundation for Sociological Understanding
The concepts explored in this chapter serve as the bedrock for understanding more complex sociological phenomena. By grasping the nuances of social interaction and the influence of culture, we can begin to unravel the mysteries of social inequality, conflict, and change.
Think of it like this: If you’re trying to build a sturdy house, you need a solid foundation. Similarly, if you want to understand the complexities of human society, you need a strong grasp of the foundational principles covered in Chapter 2. This chapter is the blueprint for understanding the social world around us.
Modern Trends and Developments: Social Interaction in a Digital Age
The digital age has added a new layer of complexity to social interaction. Social media platforms, online communities, and virtual reality experiences are reshaping how we connect, communicate, and define ourselves. These advancements raise questions about:
- The impact of social media on social norms and identity formation.
- The blurring of boundaries between real and virtual social interactions.
- The challenges of fostering genuine connection in a digitally mediated world.
Tips for Mastering Chapter 2: A Guide to Success
This chapter, though foundational, can sometimes feel overwhelming. Here are a few tips to help you navigate it effectively:
- Engage with real-life examples: Try to spot examples of social norms, status, and cultural influences in your daily life. Think about how these concepts shape your own interactions and how you interpret the world around you.
- Connect the concepts: See if you can identify how different concepts within the chapter intertwine. How do social norms relate to culture? How do social groups influence our behavior?
- Don’t be afraid to ask questions: If you find yourself struggling with a particular concept, don’t hesitate to ask your instructor or classmates for clarification.
Remember, sociology is about understanding the human experience, and that understanding starts with a firm grasp of the foundations that shape our interactions and define our social world.
FAQ: Common Questions About Chapter 2
Q: What is the difference between norms and values?
A: Norms are specific rules of behavior, like waiting in line. Values are broader ideas about what is good or bad, right or wrong; they shape the norms of a society.
Q: Is culture something we are born with or learn?
A: Culture is learned. We are born into social worlds where we absorb values, beliefs, and behaviors through interactions with others.
Q: How can I apply the concepts from Chapter 2 to my own life?
A: Pay more attention to the social norms, statuses, and cultural influences that shape your own experiences. Consider how these factors impact your choices and interactions.
Sociology Quiz Chapter 2
Conclusion
Mastering the concepts in Chapter 2 is essential for building a strong foundation in sociology. By understanding social interaction, culture, and the interplay between them, we gain a more profound understanding of the human experience and the complexities of the social world.
Are you ready to dive deeper into this fascinating world of societal foundations? Let me know if you have any questions or want to discuss any specific topics related to this chapter!






