Have you ever looked at a bar graph and felt like you were missing a piece of the puzzle? Perhaps the data seemed incomplete or you couldn’t quite grasp the full story it was trying to tell. Enter the segmented bar graph, a powerful tool that unlocks multi-faceted insights by breaking down data into its constituent parts.
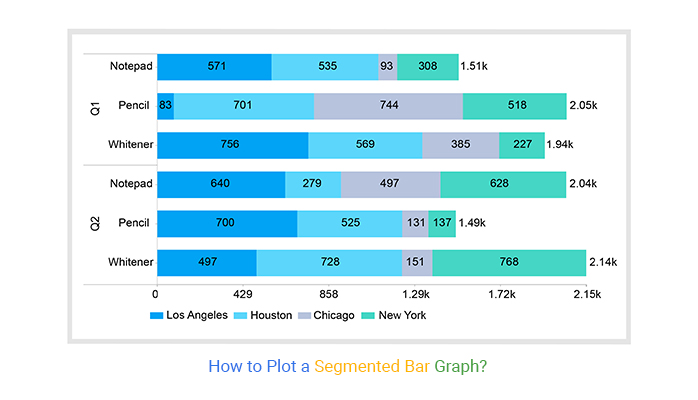
Image: chartexpo.com
Imagine you’re analyzing a company’s sales figures for different product categories. A simple bar graph might show you the total sales for each product, but it wouldn’t reveal the breakdown of sales within each category. That’s where the segmented bar graph comes in. By dividing each bar into segments representing different factors like sub-categories or sales channels, this type of graph provides a much deeper understanding of the data, revealing trends and patterns that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Understanding the Fundamentals
At its core, a segmented bar graph is a visual representation of data where each bar is subdivided into segments representing different categories or components. The size of each segment is proportional to the value it represents, allowing for easy comparison of individual components within a larger whole.
The Building Blocks of a Segmented Bar Graph
- Axis: Like any bar graph, a segmented bar graph has a horizontal (x-axis) and vertical (y-axis) axis. The x-axis usually represents categories or groups, while the y-axis represents the values being measured.
- Bars: Each bar represents a single category or group, and its height corresponds to the total value for that category.
- Segments: Within each bar, segments are used to represent different components of the total value. Each segment has a different color or pattern, making it easy to differentiate between the various components.
- Legend: A legend is included to identify the different components represented by the segments. This explains the color or pattern associated with each segment, ensuring clarity and easy understanding.
Why Choose a Segmented Bar Graph?
Segmented bar graphs offer distinct advantages over traditional bar graphs, making them valuable for a wide range of applications:
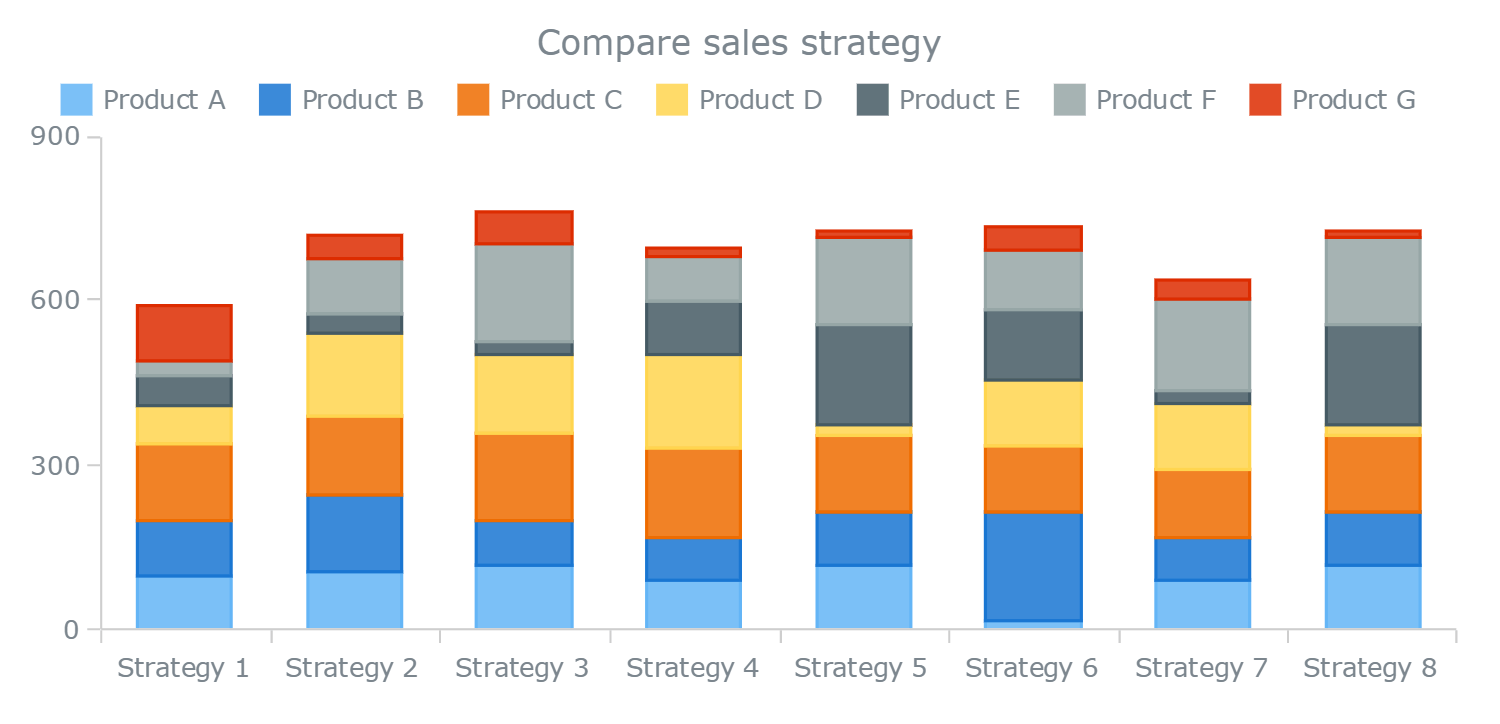
Image: jadechandler.z13.web.core.windows.net
1. Clarity and Simplicity
The segmented structure of the graph enhances visual clarity. By breaking down data into its constituent parts, it provides a better understanding of individual contributions and their relative proportions, eliminating the need for viewers to decipher complex numbers or tables.
2. Comparative Analysis
Segmented bar graphs excel in comparing different components within a category. For instance, you can easily see how sales within a particular product category are distributed across various sales channels or regions. This comparative analysis allows for deeper insights into data relationships.
3. Trend Identification
The combination of segmented data and visual representation helps identify trends over time. By comparing segments across different time periods, you can spot changes in proportions, indicating growth or decline in specific components. This aids in making informed decisions based on the observed trends.
4. Data Storytelling
Segmented bar graphs are effective tools for telling compelling data stories. By visually representing complex data in a clear and engaging manner, they captivate audience attention and convey insights powerfully. This ability to communicate data effectively is crucial for making data-driven presentations or reports.
Real-World Examples of Segmented Bar Graphs
Segmented bar graphs are widely used in various sectors for understanding and communicating complex data. Here are a few examples:
1. Marketing and Sales
A marketing team might use a segmented bar graph to analyze the performance of different advertising campaigns. Each bar could represent a specific campaign, while segments within the bar would show the breakdown of ad spend across various platforms like social media, search engines, and email marketing. This helps identify the most effective campaigns and channels for future investments.
2. Finance and Investment
Financial analysts use segmented bar graphs to illustrate a portfolio’s asset allocation. Each bar might represent an investment portfolio, with segments depicting percentages allocated to stocks, bonds, real estate, and other asset classes. The graph allows investors to quickly assess the asset allocation strategy and adjust it based on market conditions.
3. Healthcare and Demographics
Healthcare professionals use segmented bar graphs to analyze patient demographics and disease prevalence. For instance, a bar could represent a specific health condition, with segments showing the proportion of patients within different age groups or socioeconomic strata. This visual representation helps identify patient populations at higher risk and allocate resources accordingly.
4. Education and Research
Researchers and educators utilize segmented bar graphs to display data from surveys or experiments. For example, a bar could represent a particular educational program, with segments indicating the proportion of students achieving different levels of proficiency in various subjects. This allows for comparative analysis and evaluation of program effectiveness.
The Power of Segmented Bar Graphs: Beyond Simply Visualizing Data
Segmented bar graphs are more than just pretty visuals; they are powerful tools for drawing conclusions and making informed decisions. By breaking down complex data into easily understandable components, these graphs provide a clear perspective on underlying trends and patterns, enabling viewers to gain insights that might otherwise be overlooked.
Moreover, the visual nature of segmented bar graphs makes data more accessible to a wider audience, fostering effective communication and collaboration. This is particularly relevant in today’s data-driven world, where effective communication of complex insights is crucial for driving informed decision-making.
Segmented Bar Graph
Continuing to Learn and Explore
The segmented bar graph is a versatile and valuable tool for analyzing and visualizing data. As you continue to explore the world of data visualization, you’ll find that this type of graph can be applied to a wide range of scenarios, offering insights that can help you gain a deeper understanding of your data and make more informed decisions.
Remember, the key to effective data visualization is to choose the right tool for the job. While segmented bar graphs are an excellent choice for many situations, other types of charts and graphs may be more suitable depending on the nature and complexity of your data. As you become more familiar with different data visualization techniques, you’ll develop a keen eye for choosing the most effective way to present your insights clearly and effectively.






