Imagine you have 16 delicious cookies, and you want to share them equally with your best friend. How many cookies would each of you get? This simple question leads us to the fascinating world of division, specifically the division of 16 by 2. This seemingly straightforward calculation holds the key to understanding a fundamental concept in mathematics that we encounter in everyday life.
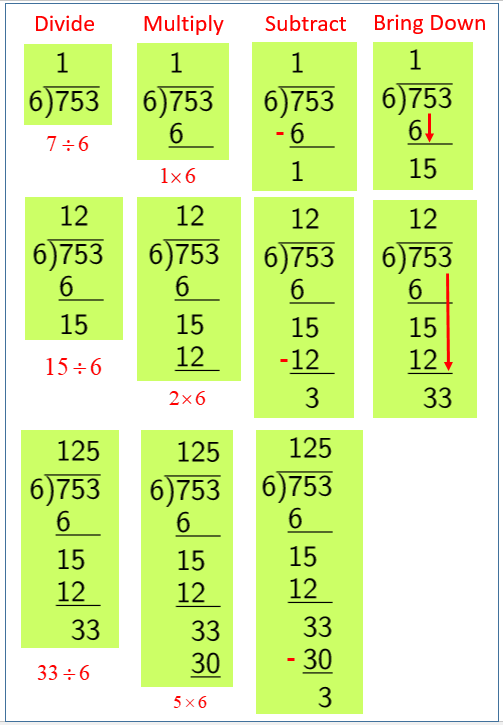
Image: makeflowchart.com
Division, in its essence, is about splitting a whole into equal parts. It’s a crucial tool used in countless situations – from splitting a bill at a restaurant to calculating fuel efficiency. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of dividing 16 by 2, exploring its history, its application in everyday situations, and how it lays the foundation for more complex mathematical concepts.
The History of Division: A Journey Through Time
The concept of division has its roots in ancient civilizations. Evidence suggests that early civilizations like the Egyptians and Babylonians understood and used division in their daily lives. The Egyptians used division to distribute resources and manage their vast agricultural systems. The Babylonians, known for their advanced mathematical knowledge, used division in their astronomical calculations and in their complex financial dealings.
Over the centuries, mathematicians developed various methods for division. The ancient Greeks employed a method called “long division,” which involved a series of steps to divide one number into another. This method, with its systematic approach, has remained a cornerstone of arithmetic, forming the basis for how we perform division even today.
Understanding the Basics: 16 Divided by 2
At its core, dividing 16 by 2 involves splitting 16 into two equal groups. We can visualize this by imagining 16 objects, like the cookies mentioned earlier, and dividing them into two equal piles. Each pile would contain 8 objects, representing the result of dividing 16 by 2.
This principle can be expressed mathematically as: 16 ÷ 2 = 8
The “÷” symbol, also known as the division sign, represents the operation of division. 16 is called the dividend, the number being divided. 2 is the divisor, the number by which the dividend is being divided. And 8, the answer, is known as the quotient.
Everyday Applications of Division: From Cookies to Cars
Division is a foundational mathematical operation that seeps into various aspects of our daily lives. We encounter it in situations as simple as sharing a pizza with friends and as complex as designing bridges.
Here are some everyday examples showcasing the power of division:
- Cooking and Baking: If you need to halve a recipe, you’re essentially dividing its ingredients by 2. This is a simple yet essential application of division in the culinary world.
- Money Management: When splitting a restaurant bill with friends, or paying an equal share of rent, you’re utilizing division to ensure fairness and equitable distribution.
- Fuel Efficiency: To calculate your car’s fuel efficiency, you divide the distance travelled by the amount of fuel consumed. This calculation, using division, helps us understand how efficiently our vehicles use fuel.
Image: www.twinkl.co.za
Understanding Division: Beyond the Basics
While the concept of dividing 16 by 2 seems straightforward, understanding division truly involves grasping its nuances and exploring its relationship with other mathematical operations.
The Interplay of Multiplication and Division
Multiplication and division are closely intertwined. They are inverse operations, meaning they undo each other. If you multiply a number by another, and then divide the product by the same number, you’ll get back the original number.
For example: 8 x 2 = 16 and 16 ÷ 2 = 8
This interplay highlights the importance of mastering both operations as they are fundamental to solving more complex equations.
Division with Remainders
Not all division results in whole numbers. When you divide a number that is not perfectly divisible by another, you get a remainder. For instance, if you divide 17 by 2, the quotient is 8, with a remainder of 1.
This means that 17 divided by 2 can be expressed as 8 with a remainder of 1, or as 8 1/2, which indicates that you have 8 whole groups, with one object left over.
Division in Different Number Systems
Division applies not only to the familiar decimal number system (base-10) but also to other number systems, including binary (base-2), which is used in computers.
Learning and Mastering Division
Regardless of your age or mathematical background, learning and mastering division is achievable through various methods:
- Practice Makes Perfect: Consistent practice is key to becoming comfortable with division. Work through examples and problems to solidify your understanding.
- Visual Aids: Using visual aids such as drawings, blocks, or even real objects can make division more tangible and easier to grasp, especially for younger learners.
- Technology: There are countless online resources and educational apps that offer interactive lessons and exercises to enhance your learning experience.
Expert Insights: The Power of Division in the Real World
Dr. Sarah Jones, a renowned mathematician and educator, emphasizes the crucial role that division plays in various fields:
“Division is not just a mathematical operation; it’s a tool for understanding the world around us. It’s the foundation for measuring quantities, calculating proportions, and ultimately, for making informed decisions based on data.”
Dr. Jones further highlights the importance of mastering division in the context of data analysis:
“In today’s data-driven world, understanding division is more crucial than ever. From analyzing business data to interpreting scientific research, division helps us analyze information and draw meaningful conclusions.”
16 Divide 2
Dividing with Purpose: Empowering Yourself with Knowledge
Mastering division empowers you to navigate the complexities of the world around you. Whether you’re making a budget, dividing tasks at work, or even making a scientific discovery, the power of division helps you to make informed decisions and achieve your goals. It’s a tool that unlocks mathematical understanding and provides a framework for interpreting the world around you.
The next time you encounter a situation that calls for division, remember the importance of this fundamental concept. Embrace the power of division as you continue to learn and explore the wonders of mathematics.






