Have you ever been planning a trip to a new country and wondered about the weather? “16 degrees Celsius, what does that even feel like?” you might ask yourself. This is a common question for those of us accustomed to the Fahrenheit scale, and it’s a great example of why understanding temperature conversions is so important. Whether you’re a traveler, a scientist, a chef, or simply someone curious about the world, knowing how to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit can make a real difference. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of temperature conversions, explaining what 16 degrees Celsius is in Fahrenheit and exploring the history, importance, and applications of these conversions.
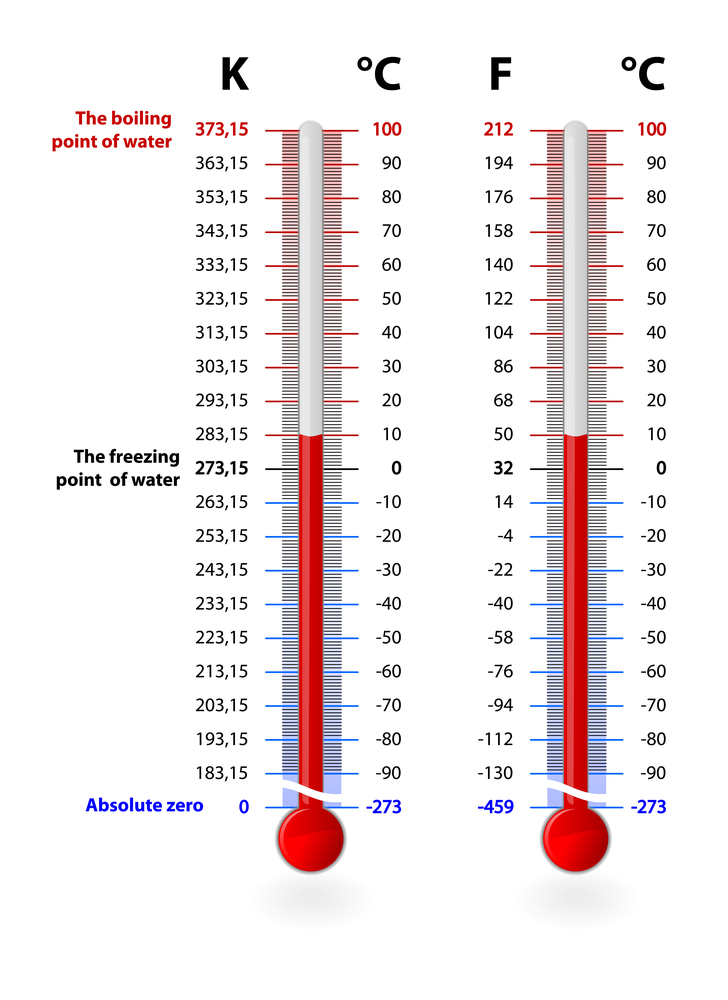
Image: www.livescience.com
The need for temperature conversions arises from the simple fact that different parts of the world use different scales. While the United States primarily uses Fahrenheit, most other countries, including Canada, Mexico, and the majority of Europe, rely on the Celsius scale. This divergence can make it tricky to comprehend weather reports, understand recipes, or even perform simple scientific experiments. That’s where understanding the relationship between Celsius and Fahrenheit comes in – it’s the bridge that connects us to a global understanding of temperature.
Celsius and Fahrenheit: A Historical Journey
To truly grasp the significance of these temperature scales, let’s take a brief journey back in time. The Celsius scale, named after Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius, was introduced in 1742. Celsius cleverly defined zero degrees as the freezing point of water and 100 degrees as its boiling point. This scale, also known as the centigrade scale, is considered a more practical system for scientific purposes because it provides a simple and logical framework for measuring temperature.
The Fahrenheit scale, on the other hand, was developed in 1724 by German physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit. This scale, which uses 32 degrees for water’s freezing point and 212 degrees for its boiling point, was initially based on a mixture of ice, water, and salt. It was originally intended for medical purposes but eventually became widely adopted in the United States.
The Conversion Formula: Unlocking the Secret
Now, let’s get to the heart of the matter: discovering what 16 degrees Celsius translates to in Fahrenheit. This is where the magic of the conversion formula comes into play. The formula for converting Celsius to Fahrenheit is:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
Let’s apply this formula to our case:
- Substitute: °F = (16°C × 9/5) + 32
- Multiply: °F = (28.8) + 32
- Add: °F = 60.8
Therefore, 16 degrees Celsius is equal to 60.8 degrees Fahrenheit.
Understanding the Conversion in Everyday Life
Beyond the formula, it’s helpful to visualize what 16 degrees Celsius actually feels like. Think of a comfortable spring day. You’d likely be wearing a light jacket or sweater, and the air would feel pleasantly cool. This is the kind of weather you’d encounter when the temperature is around 16 degrees Celsius.

Image: www.youtube.com
Practical Applications of Temperature Conversions
Now that we’ve deciphered the conversion, let’s explore some everyday scenarios where this knowledge proves invaluable:
- Travel: Imagine you’re planning a trip to Europe and see a forecast of 15 degrees Celsius. You can use the conversion formula to determine that this is equivalent to about 59 degrees Fahrenheit – a comfortable temperature for a stroll through a bustling city or relaxing in a charming café.
- Cooking: Many recipes, especially those originating from countries using the Celsius scale, will provide temperatures in Celsius. By converting these temperatures to Fahrenheit, you can ensure your dishes are perfectly cooked.
- Science: Scientists rely on temperature conversions in various disciplines, from physics and chemistry to biology and environmental studies. Understanding these conversions is crucial for accurate measurements and consistent research.
- Healthcare: In healthcare settings, precise temperature readings are essential. Medical professionals often need to convert temperatures between Celsius and Fahrenheit to ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Expert Tips for Easy Conversions
Here are some expert tips to make temperature conversions a breeze:
- Memorize a few key conversions: Familiarize yourself with some common conversions like 0°C = 32°F, 20°C = 68°F, and 30°C = 86°F.
- Use online calculators: Numerous online calculators can instantly convert temperatures between Celsius and Fahrenheit, making the process simple and convenient.
- Practice: Practice converting temperatures frequently, especially in situations where you’re likely to use them. The more you practice, the more comfortable you’ll become with the conversion process.
What Is 16 Degrees Celsius In Fahrenheit
Conclusion: Embrace the Global Language of Temperature
Understanding the conversion between Celsius and Fahrenheit empowers you to connect with the world around you. By learning about these different scales, you’ll be better equipped to interpret weather forecasts, understand scientific data, and even enjoy culinary adventures in new countries.
Whether you’re a traveler seeking adventure, a chef crafting culinary delights, a scientist conducting critical research, or simply someone curious about the world, the ability to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit is a valuable skill. So next time you encounter a temperature reading in a different scale, remember this helpful guide, and embrace the global language of temperature!






