Ever wondered what happens when things get really hot? Imagine your oven dial cranked up to 200°C, or a metal bar glowing red-hot. This seemingly simple number—200°C—represents a critical temperature threshold in countless aspects of our lives, from cooking to industrial processes to the very core of our planet.

Image:
200°C isn’t just a number on a thermometer; it’s a gateway to a world of transformations. At this temperature, materials change their properties, chemical reactions accelerate, and even life as we know it undergoes profound shifts. In this exploration, we’ll delve into the fascinating realm of 200°C, uncovering its significance in diverse fields, exploring its impact on everyday life, and discovering the mysteries it holds.
The Science Behind 200°C
To truly appreciate the impact of 200°C, we need to understand its scientific context. 200°C, or 392°F, is a temperature measured on the Celsius scale—a system widely used in science and everyday life. The Celsius scale defines 0°C as the freezing point of water and 100°C as its boiling point at standard atmospheric pressure. 200°C sits comfortably within the range where many materials and substances exhibit interesting and often dramatic changes.
Thermal Expansion
One of the most fundamental effects of heat is thermal expansion. As materials absorb heat, their molecules move faster and spread further apart, causing the material to expand in volume. This is why a metal bar gets longer when heated, why hot air balloons rise, and why a glass of water spills over when heated in the microwave. At 200°C, the expansion of many materials becomes significant, leading to noticeable changes in their dimensions and properties.
Chemical Reactions
Temperature plays a crucial role in chemical reactions. An increase in temperature typically accelerates reactions because molecules have more energy to overcome activation barriers and react. This is why food cooks faster at higher temperatures. At 200°C, many chemical reactions proceed at a rapid pace, leading to either desirable outcomes like baking bread or unwanted consequences like the combustion of flammable materials.
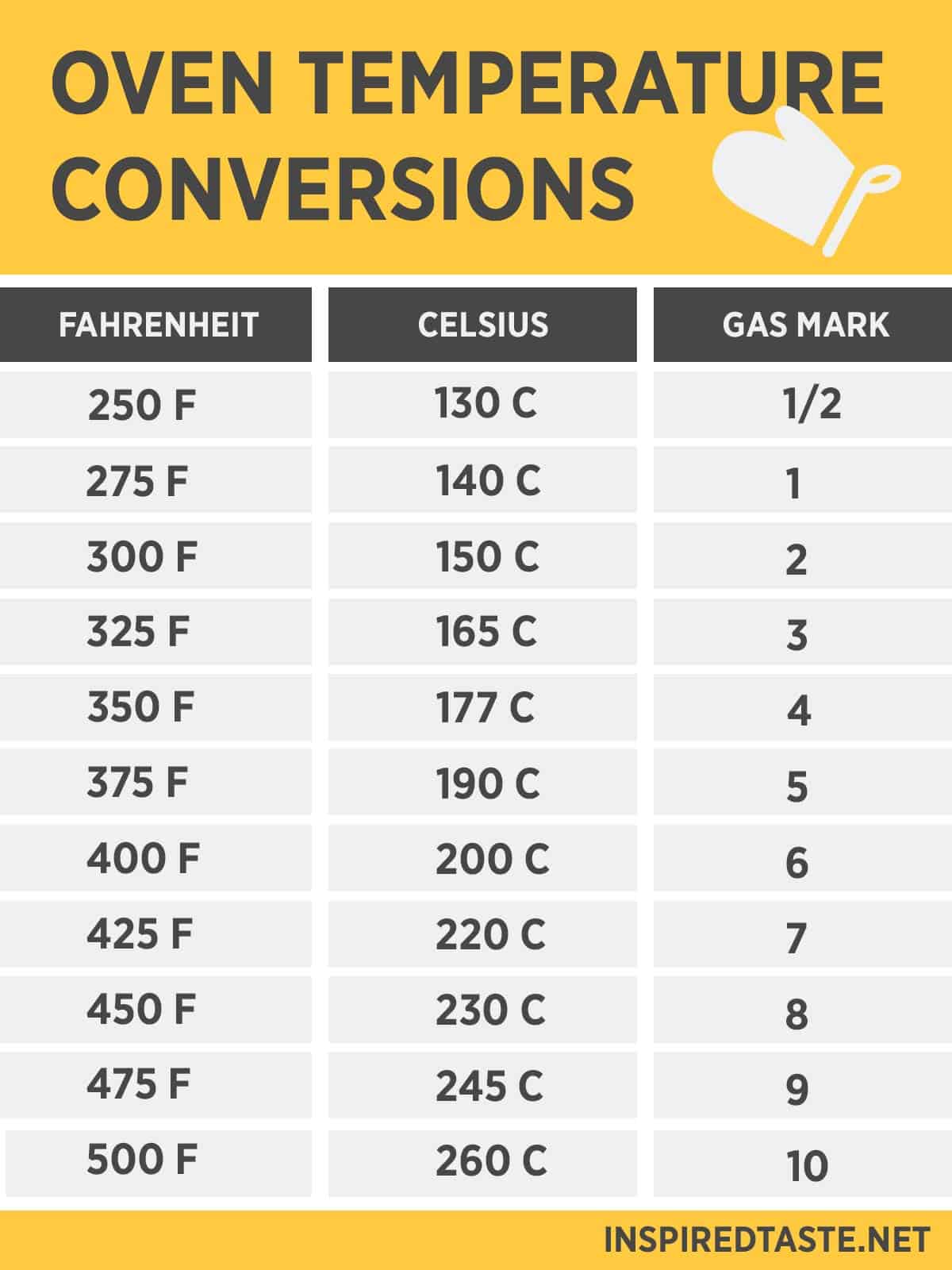
Image:
Phase Transitions
The temperature of 200°C also marks a transition point for many substances. At this temperature, some materials may transition from a solid state to a liquid state. For instance, aluminum melts at 660°C, while lead melts at 327°C. The transition from solid to liquid is particularly important in various industrial processes like metal casting and glassblowing.
200°C in Everyday Life
200°C is not just a scientific concept confined to laboratories; it plays a vital role in our everyday lives. Here are just a few examples of how 200°C impacts our daily routines:
Cooking
200°C is a common temperature for baking, roasting, and grilling. Many recipes call for oven temperatures around 200°C to ensure proper browning and cooking of meat, vegetables, and pastries. This temperature allows for efficient heat transfer and promotes the Maillard reaction, which produces the delicious browning and flavorful compounds that we associate with cooked food.
Home Appliances
Many household appliances operate at or near 200°C. Electric ovens, toasters, and hair dryers all utilize this temperature to perform their intended functions. The heating elements in these appliances reach 200°C to transfer heat efficiently and achieve the desired results, whether baking a cake, toasting bread, or drying hair.
Transportation
Cars and other vehicles use internal combustion engines that rely on controlled explosions to generate power. These explosions occur at temperatures exceeding 200°C, generating the force that drives the pistons and moves the vehicle. The engine operates within a specific temperature range, with 200°C being a critical parameter for efficient combustion and preventing overheating.
200°C in Industry and Technology
Beyond our daily lives, 200°C is a crucial factor in numerous industrial processes and technological innovations:
Metalworking
Metalworking relies heavily on the properties of metals at high temperatures. Many metals, such as steel and aluminum, are shaped, formed, and processed at temperatures around 200°C or higher. Forging, welding, and heat treatments are just a few examples of industrial processes that involve manipulating metals at elevated temperatures.
Glassmaking
Glass, a versatile and essential material, is formed and shaped at temperatures around 200°C or higher. Glassblowing, glass molding, and glass annealing all involve heating and manipulating glass to specific temperatures to obtain desired shapes and properties.
Ceramics
Ceramics, which include materials like clay, porcelain, and bricks, are manufactured and used at high temperatures. Firing ceramics in kilns at temperatures exceeding 200°C allows for the formation of strong and durable structures.
Energy Production
200°C plays a role in both traditional and renewable energy production. Power plants use steam turbines driven by boilers heated to high temperatures to generate electricity. Similarly, solar thermal power plants use mirrors to concentrate sunlight, heating a fluid to high temperatures to drive turbines and produce electricity.
200°C in the Natural World
200°C is not limited to man-made applications; it is also present in the natural world:
Volcanoes and Geothermal Activity
Volcanoes and geothermal areas are characterized by extremely high temperatures, often exceeding 200°C. The Earth’s internal heat generates molten rock, known as magma, which can reach temperatures of over 1000°C. Volcanic eruptions and geothermal vents release heat and gases, some of which reach temperatures around 200°C.
Hot Springs
Hot springs are naturally heated bodies of water that are often heated by geothermal activity. These springs can reach temperatures of 200°C or higher, providing a unique ecosystem for a variety of thermophilic organisms adapted to extreme heat.
Deep-Sea Vents
Deep-sea hydrothermal vents are openings in the ocean floor that release hot, mineral-rich fluids. These vents can reach temperatures of over 300°C, creating environments teeming with unique marine life adapted to these extreme conditions.
200c
200°C: A Temperature of Transformation and Beyond
200°C is a temperature that signifies change, transformation, and the potential for both creation and destruction. From the everyday convenience of a hot oven to the massive forces shaping our planet, 200°C plays a pivotal role in our world. As we continue to explore the mysteries of the universe and develop new technologies, 200°C and other critical temperature thresholds will continue to guide innovation and push the boundaries of our understanding of the world around us.
As we conclude this exploration into the fascinating world of 200°C, we encourage you to look around you with a renewed appreciation for the impact of this seemingly simple number. From the food we eat to the technologies that power our lives, 200°C is a constant in our world, driving progress and shaping our understanding of the universe. We invite you to share your own experiences and insights about 200°C and its significance in your life, and to continue exploring the infinite wonders of the world around us.






