Imagine a world bathed in a soft, ethereal glow, a world where the air itself shimmers with an otherworldly luminescence. This is the world of neon, a gas that has captivated humanity for centuries with its striking and enchanting light. But beyond its visual appeal lies a fascinating scientific world, where the very building blocks of this radiant element – its atoms – hold profound insights into the nature of matter itself. One of the key concepts in understanding neon is its molar mass, a seemingly simple number that unlocks secrets about the element’s behavior and its role in countless applications.

Image:
The question of how much neon weighs might seem trivial at first. After all, it’s a gas, invisible to the naked eye and seemingly weightless. Yet, this seemingly innocuous question leads us down a path of discovery, revealing the intricate world of atomic weights, chemical reactions, and the fundamental laws that govern our universe. This article will delve into the realm of molar mass, exploring its significance in the context of neon, and uncovering its critical role in shaping our understanding of this luminous element.
Exploring the Foundation: What is Molar Mass?
To comprehend the concept of molar mass, we need to first understand the building blocks of matter – atoms. Every element, from the most common hydrogen to the rarest of metals, is built from tiny, indivisible particles called atoms. Each atom has a unique atomic weight, a measure of its mass relative to a standard atom (usually carbon-12). The molar mass of an element is simply the mass of one mole of its atoms. A mole, in essence, represents a specific number of particles – 6.022 × 1023 to be exact, a number known as Avogadro’s number. This number is analogous to a dozen, which always signifies 12 objects, regardless of what those objects are. Similarly, a mole always signifies 6.022 × 1023 particles, whether they are atoms, molecules, or even elephants (though admittedly, you wouldn’t find a mole of elephants in any laboratory!).
Why is molar mass important? Imagine you’re a chef trying to bake a cake. You need a precise amount of each ingredient to ensure your cake turns out perfectly. In chemistry, molar mass acts as that precise ingredient measurement. It allows us to calculate the exact quantity of a substance needed for a chemical reaction or to understand how much of a certain element is present in a compound. Just like a skilled chef uses a recipe to guide their cooking, chemists rely on molar mass to guide their experiments.
The Glow of Discovery: Neon’s Molar Mass Unveiled
Neon, a noble gas in the second column of the periodic table, is renowned for its distinctive reddish-orange glow. This glow is what makes neon signs so captivating, illuminating our streets and cities with their vibrant colors. To understand neon’s luminescence, we need to delve into its atomic structure and its unique interaction with energy.
Neon’s atomic weight is approximately 20.18 amu (atomic mass units). This means that one atom of neon weighs approximately 20.18 times the mass of a single proton. Multiplying this atomic weight by Avogadro’s number (6.022 × 1023) gives us neon’s molar mass of approximately 20.18 grams per mole. In other words, if you were to take a sample of neon containing 6.022 × 1023 atoms, it would weigh roughly 20.18 grams.
This seemingly simple number, neon’s molar mass, holds immense power. It allows us to predict the behavior of neon in various environments – its reactions, its volume, and its density. For example, knowing neon’s molar mass allows us to calculate the mass of neon gas needed to fill a specific volume at a given temperature and pressure. This is crucial in various fields, including the design of neon signs, the production of lasers, and even the exploration of the universe.
Applications of Neon: From Neon Signs to Space Exploration
Neon’s unique properties – its inert nature, its ability to emit vivid light, and its relatively low molar mass – make it a versatile element with numerous applications. Let’s explore a few of the most prominent ways in which neon’s molar mass influences its usage.
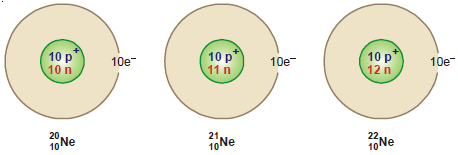
Image:
1. Neon Signs: Illuminating Our World
Neon signs are a testament to neon’s captivating allure. These iconic signs, with their bright and distinct colors, have been lighting up our streets and businesses for over a century. The glowing effect arises from the excitation of neon atoms by electrical current. When electricity passes through neon gas, the electrons in the atoms absorb energy and jump to higher energy levels. As they return to their ground state, they release energy in the form of light, producing the characteristic reddish-orange glow. Neon’s molar mass plays a critical role in this process. The lower molar mass allows for efficient energy transfer and excitation, resulting in a bright, visually appealing luminescence.
2. Lasers: Precision Light for Scientific Advancements
Neon’s use in lasers is a testament to its ability to interact with light in a controlled and predictable way. Neon lasers, especially He-Ne lasers (a mixture of helium and neon gas), are known for their stability and their ability to produce a highly focused, monochromatic beam of light. The precise wavelength of this light is crucial for applications ranging from spectroscopy to barcode scanners. The molar mass of neon plays an important role in the design and functioning of these lasers, mediating the energy transfer processes within the gas mixture and influencing the output wavelength of the laser beam.
3. Space Exploration: Unveiling the Secrets of the Universe
Neon’s presence in the universe is a testament to its abundance and its role in the cosmic dance of matter. Neon is the fifth most abundant element in the universe, after hydrogen, helium, oxygen, and carbon. Its presence in stars and nebulae provides valuable clues about their formation and evolution. Neon’s molar mass is crucial in understanding its interactions within these celestial bodies. For example, the relative abundance of neon to other elements in a star can reveal information about its age and its nuclear fusion processes. Moreover, neon isotopes (atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons) play a crucial role in tracing the history of the universe and understanding the origin of different cosmic objects.
Molar Mass Of Neon
https://youtube.com/watch?v=41AZKcktpYw
Conclusion: Molar Mass – The Unsung Hero of Neon’s Story
The molar mass of neon, while seemingly a simple numerical value, emerges as a critical player in understanding its fascinating properties and its diverse applications. From the vibrant glow of neon signs to the precise beams of lasers and the celestial insights derived from its presence in the universe, neon’s molar mass reveals its profound influence on our world and our understanding of the universe around us. This article has explored the concept of molar mass, its significance in the context of neon, and its role in shaping our understanding of this radiant element. It is a testament to the power of scientific inquiry, revealing the intricate connections between seemingly simple numbers and the wonders of the natural world.






