Ever wanted to give your photos a whole new look by transforming their colors? Maybe you want to give your landscape images a warm, golden hue, or perhaps you want to create a vibrant, fantasy-like portrait. Whatever your vision, Photoshop is a powerful tool that can help you achieve it. But getting started with color manipulation can feel intimidating, especially if you’re new to the software. Don’t worry, this guide will walk you through the basics of changing photo colors in Photoshop, step-by-step, with clear explanations and practical examples.
Image: games.udlvirtual.edu.pe
The ability to change photo colors is a core technique in digital image editing. It allows photographers and graphic designers to express their artistic vision, enhance images, create unique effects, and even correct color imbalances in photos. Whether you’re a hobbyist or a professional, mastering color manipulation in Photoshop can elevate your image editing skills and empower you to create stunning visuals.
Understanding Color Modes and Color Spaces
Color Modes
Before diving into the tools, let’s understand the foundation: color modes. Photoshop offers various color modes, each with its own characteristics and limitations. The most common color mode used for photos is **RGB**, which stands for Red, Green, and Blue. This mode represents colors by combining different intensities of red, green, and blue light. It’s ideal for displaying images on screens, as monitors use RGB light. Another important color mode is **CMYK**, used for printing. This mode uses Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Black inks to create colors.
Color Spaces
Color spaces are specific ways to define and represent colors. Different color spaces are designed for various tasks, such as printing or web design. Photoshop uses **sRGB**, a widely used color space for web and screen display, as its default workspace. For professional photography and printing, you might use **Adobe RGB** or **ProPhoto RGB**, which offer a wider range of colors. It’s important to understand the color space you are working in because it affects how your image will look on different devices and when printed.
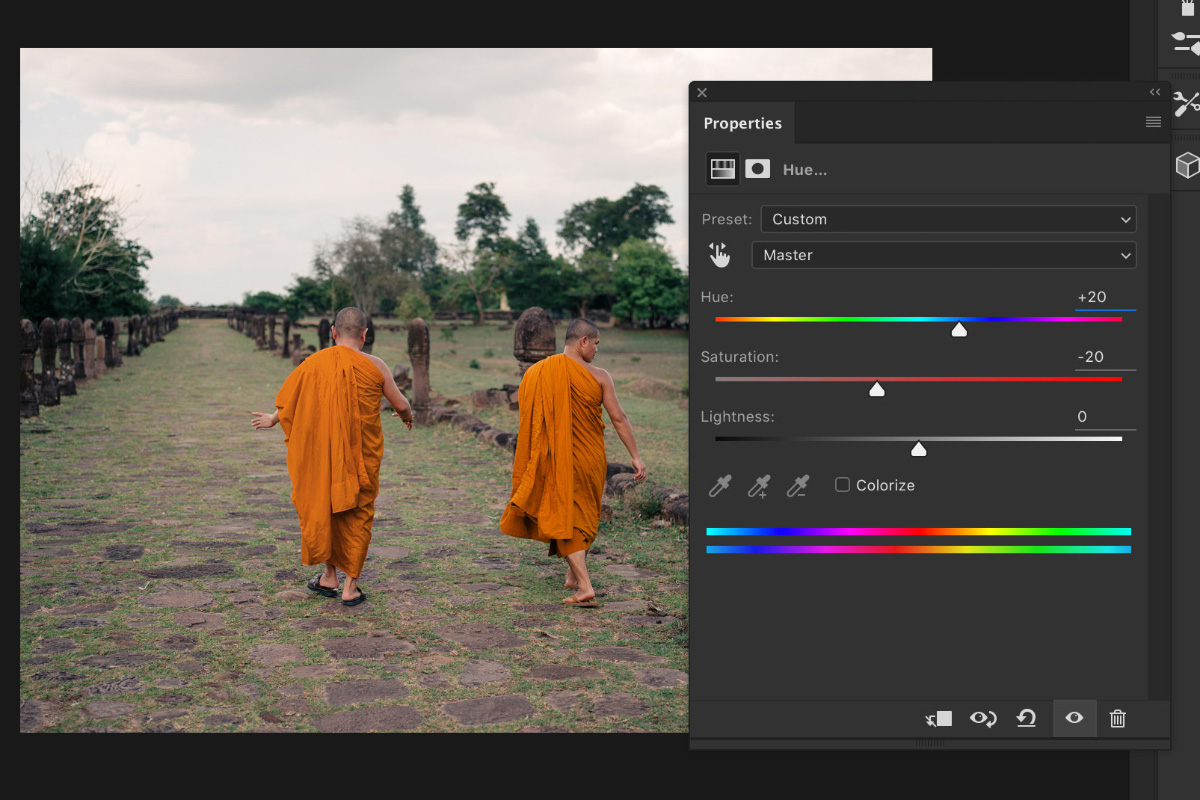
Image: expertphotography.com
Basic Methods for Changing Photo Colors
Let’s start with the fundamentals of color manipulation in Photoshop. We’ll cover four common and effective techniques:
1. Hue/Saturation Adjustment Layer
The Hue/Saturation adjustment layer is your go-to tool for making overall color shifts. It allows you to modify the hue (color), saturation (intensity), and lightness (brightness) of your image.
- **Open your image in Photoshop.**
- **Go to Layer > New Adjustment Layer > Hue/Saturation.**
- **Adjust the Hue slider to shift the colors.** The Hue slider rotates the color wheel, changing the base colors of your image.
- **Play with the Saturation slider to increase or decrease the intensity of colors.** Higher saturation makes colors more vibrant, while lower saturation makes them muted.
- **Use the Lightness slider to make the image brighter or darker.** Increase the lightness to make the image lighter, decrease for a darker look.
This layer is non-destructive, meaning it doesn’t directly modify your original image pixels. It creates a separate layer that you can adjust or delete without permanently affecting your photo.
2. Color Balance Adjustment Layer
The Color Balance adjustment layer lets you fine-tune the balance of colors in your image by adjusting the levels of red, green, and blue. It’s excellent for correcting color casts, such as a warm orange tint in a photo taken under artificial light.
- **Create a Color Balance adjustment layer.** (Layer > New Adjustment Layer > Color Balance)
- **Choose the “Midtones” option to adjust the overall image colors.** You can also choose “Shadows” or “Highlights” to focus on specific tonal ranges.
- **Slide the red, green, and blue sliders to adjust the color balance.** For example, adding more red to midtones can create a warmer image, while adding more blue can create a cooler look.
3. Selective Color Adjustment Layer
The Selective Color adjustment layer is ideal for fine-tuning the color of specific color ranges within your image. It lets you control how much of each primary color (cyan, magenta, yellow, black) is present in chosen color ranges (red, yellow, green, cyan, blue, magenta, black, white).
- **Create a Selective Color adjustment layer.** (Layer > New Adjustment Layer > Selective Color)
- **Select a color range (e.g., Reds) from the dropdown menu.**
- **Use the sliders for cyan, magenta, yellow, and black to change the color of that specific range.** Adding more cyan to the Reds range, for example, will move the reds towards a bluer hue.
4. Color Replacement Tool
The Color Replacement tool is a handy way to change the hue of a specific area of your image while retaining the original image’s details and textures. It’s useful for replacing a particular color with a new one, like changing the color of a shirt in a photo.
- **Select the Color Replacement tool from the tools panel.**
- **Choose a foreground color in the Color Picker.** This will be the new color that replaces the selected color.
- **Adjust the tool’s settings:**
- **Tolerance:** Controls how similar colors are included in the replacement. A higher tolerance includes more colors.
- **Sampling:** Choose how to determine what colors to replace.
- **Localized Color:** Determines if only the chosen color or all similar colors are replaced.
- **Click and drag over the area you want to color replace.** The tool will replace the colors within your selected area.
Advanced Techniques for Color Manipulation
Once you’ve grasped the basics, you can explore more advanced techniques for color transformation:
1. Channel Mixer
The Channel Mixer is a powerful tool that lets you combine the red, green, and blue channels of your image to create dramatic color effects. It’s useful for creating black and white images, adding color tints to your photos, and changing the overall color temperature.
- **Create a Channel Mixer adjustment layer.** (Layer > New Adjustment Layer > Channel Mixer)
- **Choose the “Monochrome” checkbox if you want to create a black and white image.**
- **Adjust the sliders for the red, green, and blue channels to change the color mix. ** For example, to create a sepia tone, you would increase the red channel and decrease the blue channel.
2. Gradient Map
The Gradient Map is a non-destructive way to apply a color gradient to your image. It maps the tonal range of your image to a gradient, so the darkest areas of the image will match the darkest color in the gradient, and the brightest areas will match the lightest color. This is a great option for creating artistic effects or adding color to black and white images.
- **Create a Gradient Map adjustment layer.** (Layer > New Adjustment Layer > Gradient Map)
- **Choose a gradient from the Gradient Picker. ** You can also create your own gradients by adding color stops to the gradient bar.
- **Adjust the gradient map settings:**
- **Reverse:** Flips the gradient.
- **Dither:** Reduces banding in the gradient.
3. Color Lookup Tables (LUTs)
LUTs offer a quick and efficient way to apply pre-defined color transformations to your images. They allow you to transform the color of an image based on a predefined set of color mappings. You can find LUTs online or create your own for specific looks.
- **Go to Layer > New Adjustment Layer > Color Lookup.**
- **Click on the “3DLUT File” dropdown menu and choose a LUT.**
- **Experiment with different LUTs and find the one that best suits your desired effect.**
Tips for Effective Color Manipulation
Here are some helpful tips for getting the most out of Photoshop’s color manipulation tools:
- Use Adjustment Layers. Adjustment layers are non-destructive, allowing you to experiment with different adjustments without permanently altering your image. You can always go back, adjust the settings, or delete the layer if you don’t like the results.
- Start with a Good Image: A well-exposed and well-composed image will produce better results. If your image has significant color casts or problems with white balance, try correcting those issues first before attempting color manipulation.
- Experiment with Multiple Tools: Don’t be afraid to try different adjustment layers and tools to achieve your desired color look. Sometimes, combining multiple techniques can create more nuanced and interesting effects.
- Use Color Swatches: Photoshop includes various color swatches that can help you choose harmonious and complementary colors. You can also create your own custom swatches, which is especially useful if you’re working with specific brand colors or design guidelines.
- Work with Layers: Using layers to apply multiple color adjustments allows you to isolate each change and fine-tune them independently.
- Use Color Picker: If you need to sample a specific color from your image, use the Color Picker tool. This is helpful for creating consistent colors across your image or for finding complementary colors.
- Consider Color Theory: Understanding color theory can help you make more informed decisions about color manipulation. This knowledge can guide you in choosing colors that complement each other, create a specific mood, or improve the overall aesthetic of your image.
How To Change Color Of Picture In Photoshop
Conclusion
Mastering the art of color manipulation in Photoshop opens up a world of possibilities for creating stunning and expressive images. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to refine your skills, this guide has provided a comprehensive overview of techniques and tips. Remember, practice is key to mastering these tools! The more you experiment, the more comfortable you’ll become with applying color changes to your photos. So go ahead, grab an image and unleash your creative potential by exploring the vast palette of color manipulation in Photoshop! And if you have any questions, don’t hesitate to ask for help from the vibrant online community of Photoshop users. Good luck and have fun!






